Cellular Respiration
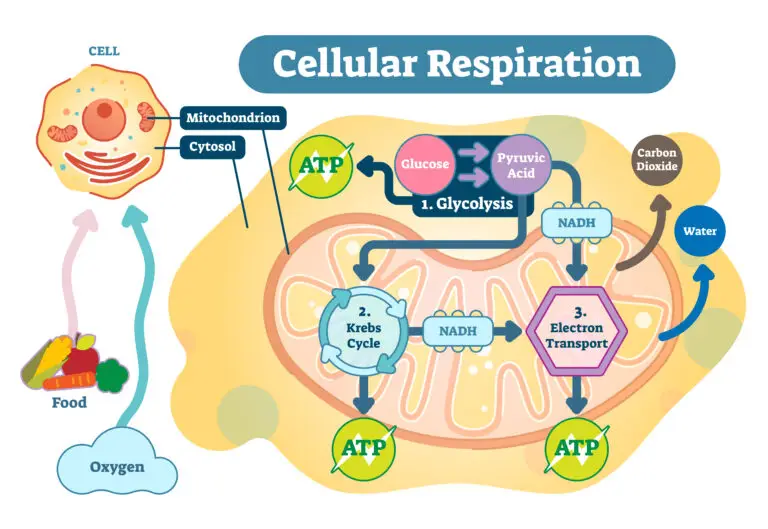
Table of Contents
What is Cellular Respiration?
Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic processes that occur within cells, converting biochemical energy derived from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy currency of cells.
This process occurs in three main stages: glycolysis, the citric acid (Krebs cycle), and oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport chain and chemiosmosis). Cellular respiration is a fundamental process for energy production in eukaryotic cells, enabling them to carry out various activities and functions.
Overview of Cellular Respiration
Glycolysis
- Location: Takes place in the cytoplasm.
- Process: Glucose, a six-carbon sugar, is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate, a three-carbon compound.
- ATP Production: Generates a small amount of ATP directly.
During glycolysis, glucose is oxidized and converted into two molecules of pyruvate, while ATP and NADH molecules are produced.
Citric Acid Cycle (Krebs Cycle)
- Location: Takes place in the mitochondria.
- Process: Each pyruvate molecule from glycolysis is further broken down, releasing carbon dioxide and producing NADH and FADH2.
- ATP Production: Generates a small amount of ATP directly.
Oxidative Phosphorylation
- Location: Takes place in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
- Process: NADH and FADH2 produced in glycolysis and the citric acid cycle donate electrons to the electron transport chain (ETC).
- ATP Production: The electron transport chain facilitates the flow of electrons, leading to the pumping of protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane. This sets up a proton gradient, and ATP is synthesized through chemiosmosis.
Overall Equation
The overall chemical equation for cellular respiration is:
C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6 O2 (oxygen) → 6 CO2 (carbon dioxide) + 6 H2O (water) + ATP (energy)
Aerobic vs. Anaerobic Respiration
- Aerobic Respiration: Requires oxygen and is more efficient, producing a larger amount of ATP.
- Anaerobic Respiration: Occurs in the absence of oxygen and typically involves fermentation. It is less efficient in terms of ATP production.
Significance
Cellular respiration is the fundamental process through which cells extract energy from nutrients, primarily glucose, to perform essential functions. This multi-step process involves the breakdown of glucose molecules in the presence of oxygen to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the cell’s energy currency. ATP is then utilized by cells to power various activities, including growth, maintenance, repair, and the synthesis of biomolecules like proteins and nucleic acids.
Related Links
What are Cells?
What is Cytoplasm?
What is Mitochondria?
What is Respiration?