Deoxyribose
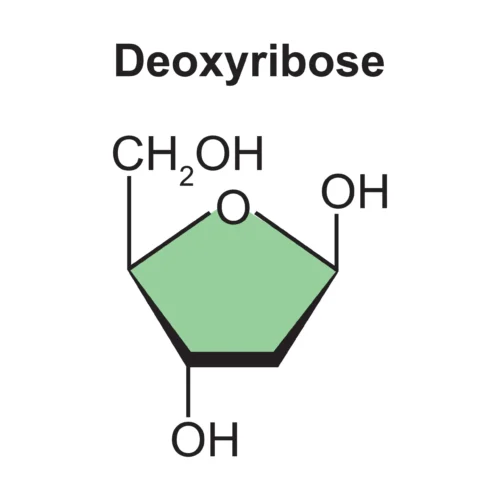
Table of Contents
What is Deoxyribose?
Deoxyribose is a sugar molecule that forms part of the backbone structure of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). It is a modified form of ribose, which is a five-carbon sugar. The main difference between deoxyribose and ribose lies in the presence or absence of an oxygen atom at the 2′ position of the sugar ring.
Deoxyribose lacks oxygen at this position, so it is called “deoxy” (meaning without oxygen) ribose.
Deoxyribose Structure Overview
Structure
- Deoxyribose is a pentose sugar with five carbon atoms in its ring structure.
- Its chemical formula is C5H10O4.
- The carbon atoms are numbered from 1′ to 5′, and the oxygen atom is absent at the 2′ position in deoxyribose.
Role in DNA
Deoxyribose is a fundamental component of the DNA molecule, forming the sugar-phosphate backbone and phosphate groups. The linkage between deoxyribose molecules involves phosphodiester bonds, creating a stable and linear structure.
DNA Nucleotides
In DNA, each deoxyribose molecule is associated with one of the four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), or guanine (G). A DNA nucleotide consists of a deoxyribose sugar, a phosphate group, and one of the four nitrogenous bases.
Genetic Information
The sequence of deoxyribose sugars and associated nitrogenous bases along the DNA strands carries genetic information. The specific sequence of nucleotides determines the genetic code, and this information is essential for the synthesis of proteins and other cellular functions.
RNA vs. DNA
RNA (ribonucleic acid) contains ribose sugar instead of deoxyribose. The key distinction is the presence of an additional oxygen atom at the 2′ position in ribose.
Related Links
Base Pair
Denaturation
RNA
Nucleotide