Excretion
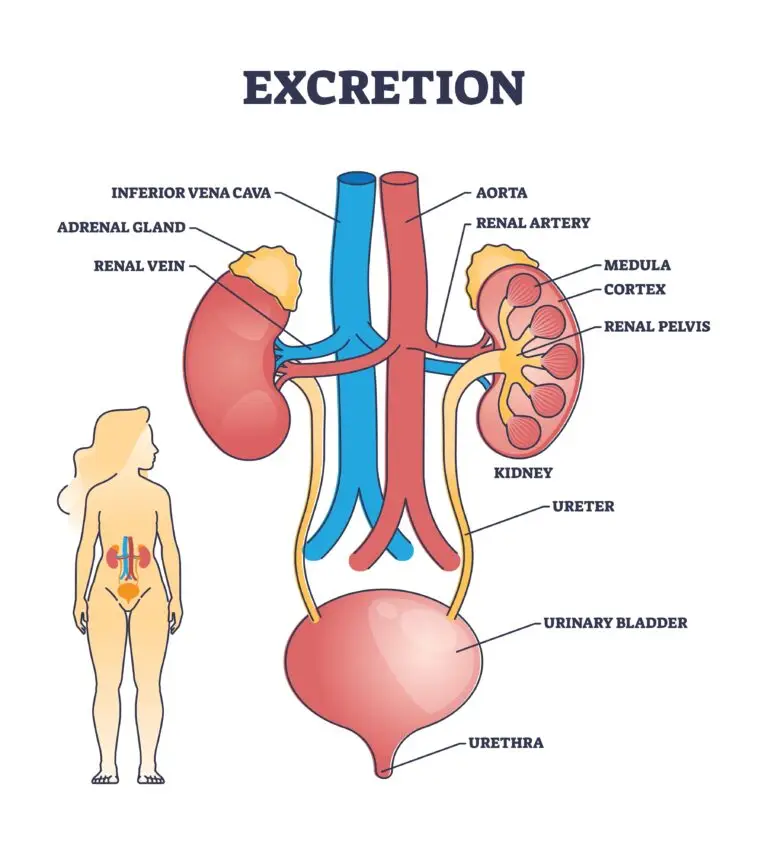
Table of Contents
What is Excretion?
Excretion is the biological process by which waste products of metabolism, and other non-essential substances are eliminated from an organism. It is a vital physiological process that helps maintain homeostasis by removing harmful or excess substances from the body, ensuring the internal environment remains balanced.
The Excretion Process
Waste Products
Excretion involves the removal of waste products generated by metabolic processes within cells. These waste products may include nitrogenous compounds, such as urea and ammonia, produced during the breakdown of proteins.
Metabolic Waste
Metabolic waste products are by-products of cellular activities, and their accumulation can harm the organism. Excretion prevents the buildup of these substances in the body.
Organs of Excretion
Various organs and structures contribute to the excretory process in different organisms:
- In humans and many animals, the kidneys are central in filtering blood and excreting waste products in urine.
- The liver is involved in breaking certain toxins and producing bile, which is excreted into the digestive system.
- The skin excretes sweat, which contains water, electrolytes, and small amounts of metabolic waste products.
- The lungs excrete carbon dioxide, a waste product of cellular respiration.
Regulation of Water and Electrolytes
Excretion is closely linked to the regulation of water and electrolyte balance in the body. Kidneys play a crucial role in maintaining the appropriate concentration of ions and water in the blood.
Excretory Systems in Plants
In plants, excretion involves the elimination of waste products and excess substances. Plants excrete oxygen produced during photosynthesis and may also excrete substances into the soil through root exudates.
Related Links
Catalyst (Biology)
Digestion
Enzyme
Lysosome