Frond
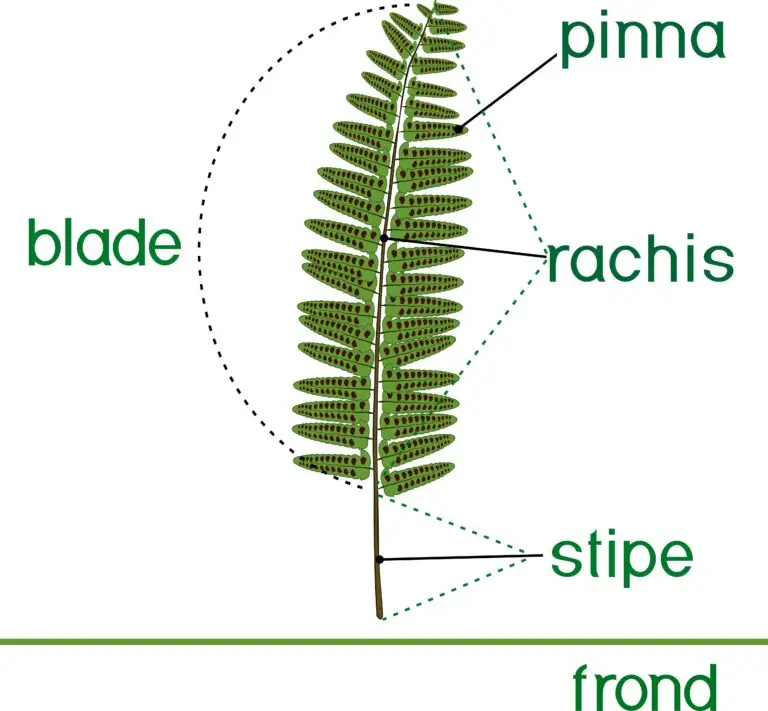
Table of Contents
What is a Fond?
The term “frond” refers to a large, often divided leaf, especially in the context of ferns and certain other plants. Fronds are typically associated with plants that reproduce via spores and exhibit a characteristic leaf structure distinct from flowering plants’ leaves.
Characteristics of Fronds
Leaf Structure
Fronds are large and compound leaves, meaning they are divided into multiple smaller leaflets or pinnae. The arrangement of the leaflets gives the frond a feathery or fern-like appearance.
Spore Reproduction
Plants with fronds, such as ferns, reproduce via spores rather than seeds. Spores are tiny, reproductive cells produced on the undersides or edges of the fronds.
Vascular Tissues
Fronds, like other leaves, contain vascular tissues that facilitate the transport of water, nutrients, and photosynthetic products throughout the plant.
Photosynthesis
Fronds play a crucial role in photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy. The large surface area of fronds allows for optimal light absorption.
Arrangement and Shape
The arrangement and shape of fronds can vary among different plant species. Some fronds may be simple, while others are highly divided with a pinnate or palmate arrangement.
Examples of Plants with Fronds
Ferns: Ferns are a prominent group of plants known for their fronds. Fern fronds are often found in damp or shaded environments. Examples include the Boston fern and the sword fern.
Cycads: Cycads, a group of seed plants with a long evolutionary history, also produce fronds. Cycad fronds are often large and pinnately divided.
Palms: Some palm trees have leaves that are referred to as fronds. Depending on the palm species, these fronds can be large, fan-shaped, or pinnately divided.
Horsetails (Equisetum): Horsetails are a group of non-flowering vascular plants that produce jointed stems with small-scale-like leaves arranged in whorls. The stem resembles a hollow jointed stalk with a cone-like structure at the tip.
Related Links
Botany
Cellular Respiration
Herbivore
The Photosynthesis Process