Gene Expression
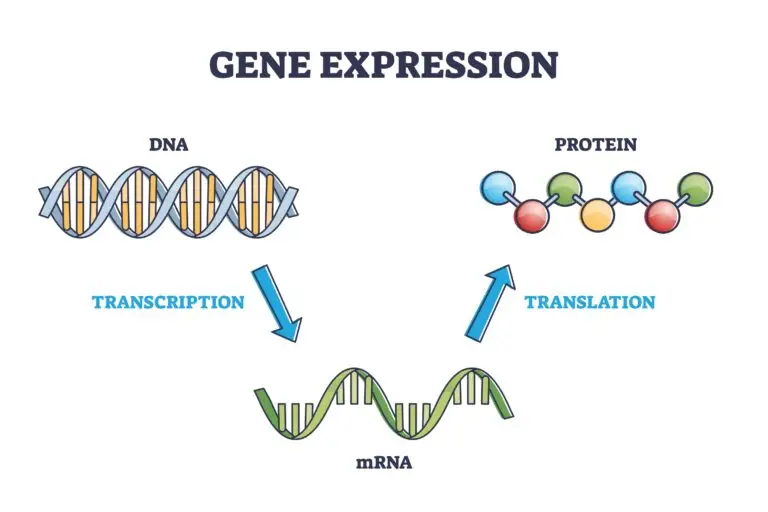
Table of Contents
What is a Gene Expression?
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used to synthesize a functional gene product, such as a protein or functional RNA molecule. It involves the transcription of the genetic code stored in DNA into RNA and the subsequent translation of RNA into a functional product.
Gene expression is a fundamental biological process that allows cells to carry out the instructions encoded in their genes, determining the characteristics and functions of an organism.
Gene Expression Overview
Transcription
Transcription is the first step in gene expression, where the information stored in a DNA sequence is transcribed into a complementary RNA sequence. This process occurs in the cell nucleus and is catalyzed by RNA polymerase.
mRNA (Messenger RNA)
The transcribed RNA molecule, known as messenger RNA (mRNA), carries the genetic information from the DNA to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm, where protein synthesis will take place.
Translation
Translation is the second step in gene expression, where the information in mRNA is used to synthesize a specific protein. This process occurs on ribosomes in the cytoplasm. Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules bring amino acids to the ribosome, and the mRNA sequence is translated into a corresponding sequence of amino acids.
Protein Synthesis
During translation, the ribosome reads the mRNA sequence in sets of three nucleotides called codons. Each codon corresponds to a specific amino acid or a signal to start or stop protein synthesis.
The amino acids brought by tRNA molecules are linked together to form a polypeptide chain, which then folds into a functional protein.
Regulation of Gene Expression
Gene expression is highly regulated to ensure that specific genes are activated or repressed in response to cellular needs and environmental cues. Regulation occurs at various levels, including transcriptional, post-transcriptional, translational, and post-translational levels.
Gene Regulatory Elements
DNA sequences contain regulatory elements, such as promoters and enhancers, that control the initiation of transcription. Binding of regulatory proteins to these elements influences the rate at which genes are transcribed.
Related Links
Dominant Traits
Translation
Recombinant DNA
RNA