Hormone
Table of Contents
What are Hormones?
A hormone is a regulatory signaling molecule produced by glands in multicellular organisms, including animals and plants. Hormones serve as messengers that travel through the bloodstream to target cells or organs, exerting specific effects on physiological processes, growth, development, metabolism, and behavior.
Understanding Hormones
Chemical Messengers
Hormones are chemical messengers that transmit signals within the body. They are produced by specialized cells or glands and are released into the bloodstream.
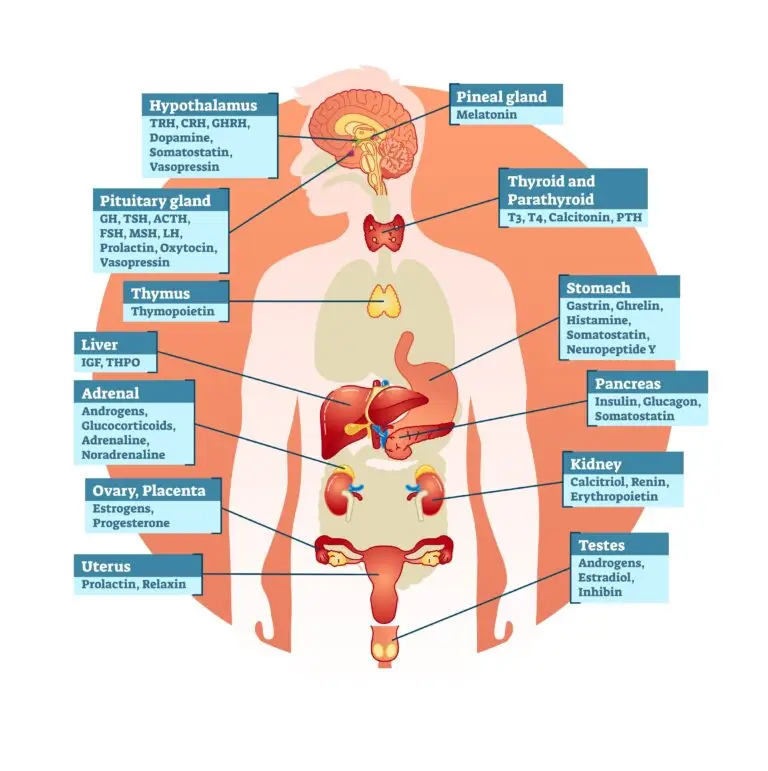
Endocrine System
The endocrine system is the primary system involved in hormone regulation. It consists of glands (such as the pituitary, thyroid, adrenal glands, and others) that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream.
Target Cells or Organs
Hormones travel through the bloodstream and bind to specific receptors on target cells or organs. These receptors are proteins part of the target’s cellular membrane or interior.
Regulation of Physiological Processes
Hormones play a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes, including metabolism, growth and development, immune function, reproductive processes, and responses to stress.
Classes of Hormones
Hormones can be classified based on their chemical structure and function. The main classes include peptides and proteins (e.g., insulin, growth hormone), steroids (e.g., cortisol, estrogen, testosterone), and amines (e.g., adrenaline, thyroid hormones).
Examples of Hormones
Examples of hormones include insulin (regulates blood sugar levels), adrenaline (produced in response to stress), thyroid hormones (regulates metabolism), estrogen and testosterone (regulates reproductive processes), and growth hormone (stimulates growth and development).
Related Links
Homeostasis
Homologous
Immune System
Pathogen