Metabolism
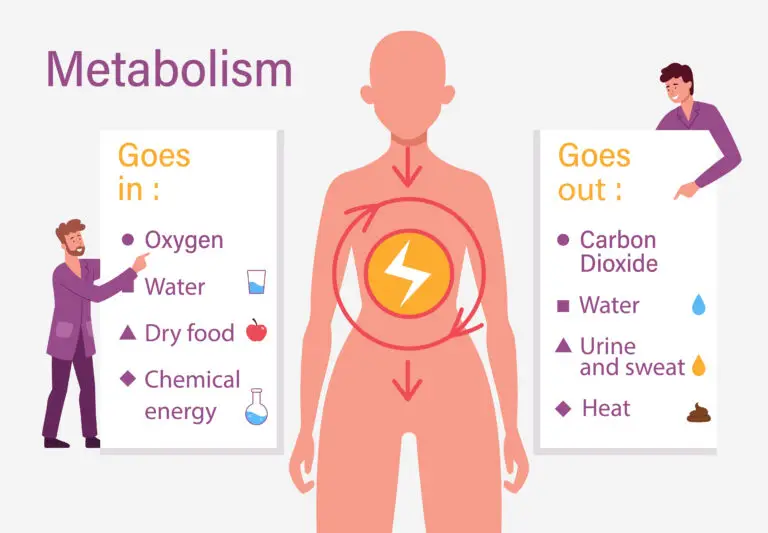
Table of Contents
What is Metabolism?
Metabolism refers to the chemical reactions occurring within living organisms to maintain life. These biochemical processes allow organisms to acquire energy, utilize nutrients, and synthesize and break down molecules necessary for growth, maintenance, and reproduction.
Metabolism encompasses both anabolism (building complex molecules from simpler ones) and catabolism (breaking complex molecules into simpler ones).
Process of Metabolism
Energy Acquisition and Utilization
One of the primary functions of metabolism is to acquire and utilize energy. Organisms need energy for various cellular activities, such as maintaining cell structure, transporting molecules across membranes, and carrying out mechanical work.
Nutrient Processing
Metabolism involves the processing of nutrients obtained from the environment. These nutrients include carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, vitamins, and minerals. Through metabolic pathways, these nutrients are broken down to release energy or used to build complex molecules.
Anabolism (Biosynthesis)
Anabolic pathways involve the synthesis of complex molecules from simpler ones. Examples include the synthesis of proteins from amino acids, the formation of DNA and RNA from nucleotides, and the production of complex carbohydrates.
Catabolism (Degradation)
Catabolic pathways involve the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler ones, releasing energy in the process. For example, the breakdown of glucose through cellular respiration releases energy that is used by the cell.
Enzymatic Reactions
Metabolic reactions are facilitated by enzymes, which act as biological catalysts. Enzymes accelerate the rate of chemical reactions without being consumed in the process. A specific enzyme often catalyzes each step of a metabolic pathway.
Adaptation to Environmental Conditions
Metabolic processes can be influenced by environmental factors such as temperature, availability of nutrients, and oxygen levels. Organisms may adjust their metabolic activities to adapt to changing conditions.
Related Links
Catalyst (Biology)
Excretion
Hormone
Urea