Niche
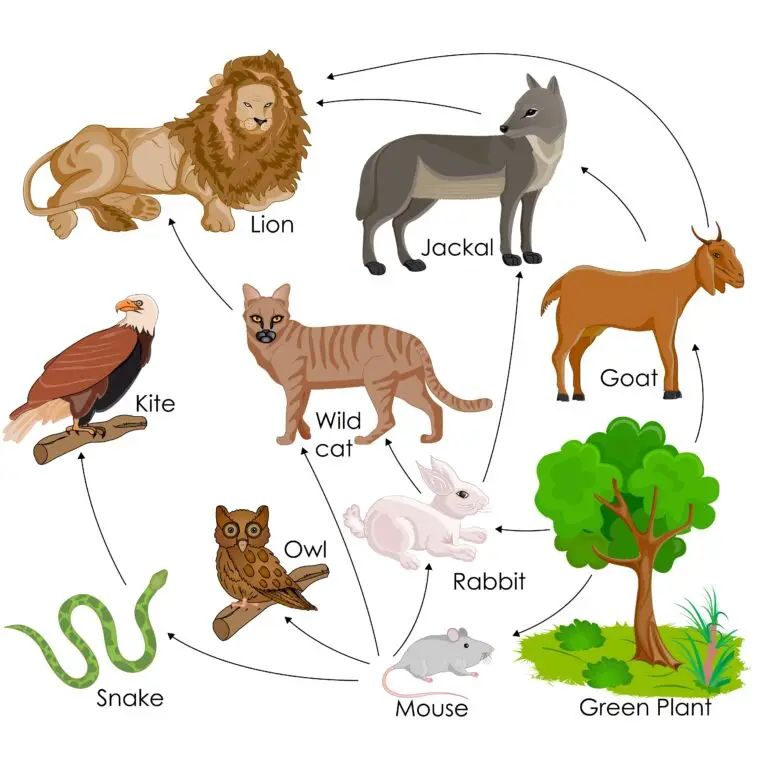
Table of Contents
What is a Niche?
A niche refers to the role or function of an organism or species within an ecosystem. It encompasses how an organism obtains its energy and nutrients, where it lives, how it interacts with other organisms, and its influence on the environment. The niche concept is fundamental to understanding the ecological relationships and dynamics within ecosystems.
Key Aspects of a Niche
Habitat
The physical space or environment where an organism lives is part of its niche. This includes the specific geographical location, climate, and conditions necessary for the organism’s survival.
Feeding Relationships
The niche describes how an organism obtains its energy and nutrients. This involves the type of food it consumes, its feeding habits, and its position in the food web or trophic level.
Reproductive Strategy
The niche includes aspects of an organism’s reproductive behavior, such as when and how it reproduces, the number of offspring produced, and parenting behaviors.
Interactions with Other Species
The niche considers how an organism interacts with other species in its environment. This involves both symbiotic relationships (mutualism, commensalism, or parasitism) and competitive interactions for resources.
Behavioral Adaptations
Niche also encompasses an organism’s behavioral adaptations, such as its activity patterns, mating rituals, and responses to environmental stimuli.
Role in Ecosystem Dynamics
Understanding an organism’s niche is crucial for predicting its impact on ecosystem dynamics. It helps ecologists study how changes in one species or environmental factor can affect the entire ecosystem.
Types of Niches
- Fundamental Niche: The theoretical, idealized niche that an organism could occupy without competition or other ecological constraints.
- Realized Niche: The actual niche that an organism occupies, considering factors such as competition with other species and environmental limitations.
- Ecological Niche: A broader concept that encompasses the entire range of conditions and resources an organism can use or tolerate. It includes both abiotic (non-living) and biotic (living) factors.
- Grinnellian Niche: Focuses on the physical and environmental aspects of a niche, such as habitat requirements and climate tolerances.
- Eltonian Niche: Emphasizes the role of an organism within its community and its interactions with other species.
Examples of Niche
- The niche of a predator, like a lion, includes its role in the food web, its hunting behavior, and its impact on prey populations.
- The niche of a tree species in a forest includes its habitat preferences, the types of nutrients it requires, and its interactions with other plants for sunlight and nutrients.
Related Links
Community
Competition
Omnivore
Symbiosis