Parasite
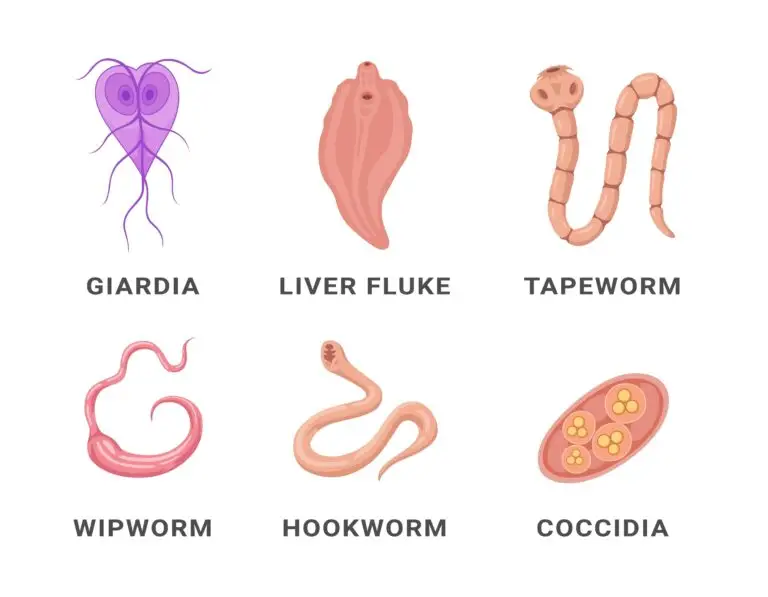
Table of Contents
What is a Parasite?
A parasite is an organism that lives in or on another organism (host) and derives nutrients and sustenance at the expense of the host. The relationship between a parasite and its host is often characterized by the parasite benefiting, while the host is harmed to varying degrees. Parasites can be found in various forms, including microscopic organisms, worms, insects, and even certain plants.
Key Features of Parasites
Host Dependency
Parasites are dependent on their host for survival. They rely on the host’s resources, such as nutrients, energy, and shelter, to complete their life cycle.
Harm to the Host
Parasitism typically involves some degree of harm or damage to the host. The harm can range from mild inconvenience to severe illness or death, depending on the type of parasite and the intensity of the infection.
Adaptations for Parasitism
Parasites often have specific adaptations that allow them to exploit their hosts. These adaptations may include specialized structures for attachment, mechanisms to evade the host’s immune system, and complex life cycles that involve multiple hosts.
Transmission
Parasites often have mechanisms for transmitting themselves to new hosts. This can occur through various means, such as direct contact between hosts, ingestion of contaminated food or water, or through intermediate hosts in complex life cycles.
Types of Parasites
Parasites can be broadly categorized into different types based on their relationships with hosts:
- Ectoparasites: Live on the surface of the host’s body (e.g., ticks, lice).
- Endoparasites: Live inside the host’s body (e.g., intestinal worms, protozoa).
- Facultative Parasites: Can live independently but may become parasitic under certain conditions.
- Obligate Parasites: Depend entirely on the host for survival.
Examples of Parasites
- Protozoa: Plasmodium species causing malaria.
- Helminths: Roundworms, tapeworms, and flukes.
- Arthropods: Fleas, ticks, lice, and mites.
- Microorganisms: Bacteria, viruses, and fungi can also exhibit parasitic behavior.
Related Links
Antigen
Pathogen
Symbiosis
Virus