Prophase
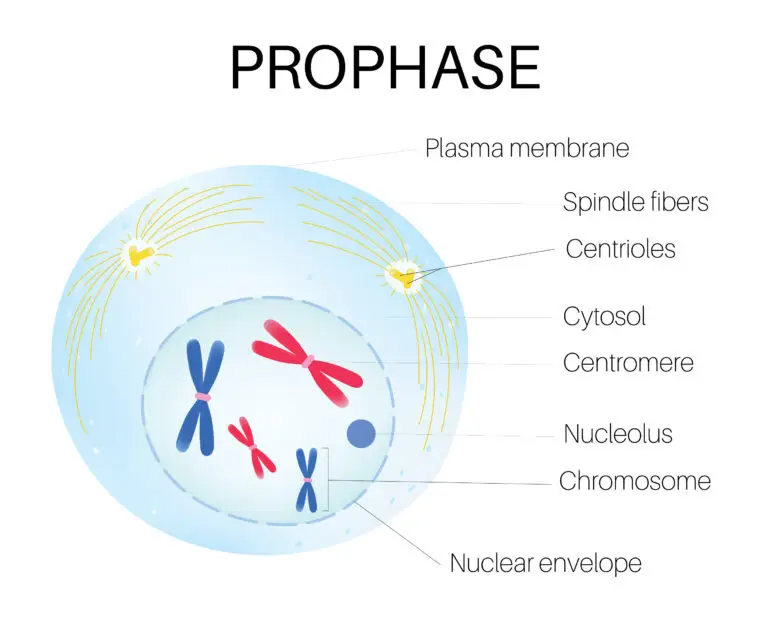
Table of Contents
Prophase Definition
Prophase is the first stage of mitosis, a process of cell division that forms two genetically identical daughter cells. Mitosis is crucial for the growth, repair, and maintenance of multicellular organisms. Prophase is characterized by significant changes in the cell’s nucleus and other cellular structures as the cell prepares for division.
Overview of Prophase
Chromatin Condensation
In interphase, the DNA exists as chromatin – a complex of DNA, RNA, and proteins. During prophase, chromatin condenses into visible structures called chromosomes. Each chromosome consists of two identical sister chromatids held together by a centromere.
Formation of Mitotic Spindle
Microtubules, part of the cytoskeleton, begin to reorganize into a structure known as the mitotic spindle. The spindle fibers extend from structures called centrosomes, which are involved in organizing and anchoring the microtubules.
Nuclear Envelope Breakdown
The nuclear envelope, which surrounds the nucleus in interphase, starts to disintegrate during prophase. This breakdown allows the mitotic spindle to access the chromosomes.
Centrosome Movement
The centrosomes, each containing a pair of centrioles, move to opposite poles of the cell. As they move, they contribute to the organization of the mitotic spindle.
Kinetochores
Kinetochores, protein structures on the centromeres of chromosomes, form during prophase. They serve as attachment points for spindle fibers, facilitating the movement of chromosomes.
Significance of Prophase
Prophase marks the initiation of mitosis, where the cell undergoes significant changes to prepare for division. The condensation of chromatin into visible chromosomes and the organization of the mitotic spindle are crucial events that set the stage for the subsequent orderly separation of genetic material into two daughter cells.
Related Links
Karyotype
Metaphase
Meiosis
Telophase