Reproduction
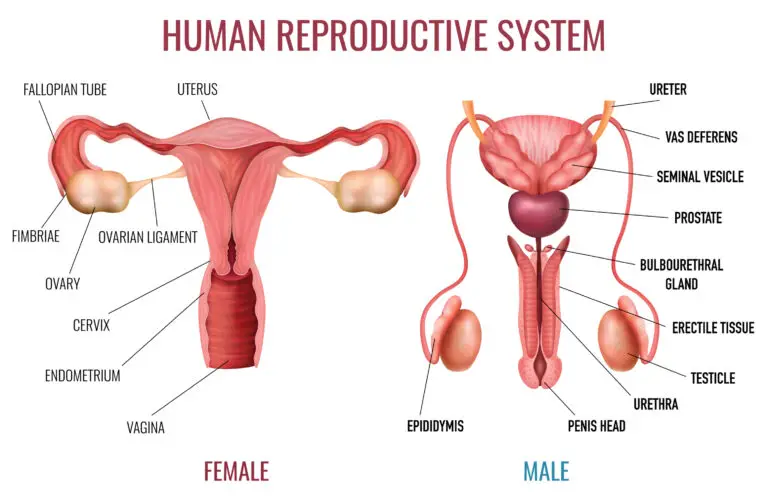
Table of Contents
What is Reproduction?
Reproduction is a biological process by which new individuals of the same species are produced, ensuring the continuation of the species over generations. Reproduction is a fundamental characteristic of living organisms and is essential for the survival and evolution of species. There are two main types of reproduction: asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction.
Significance of Reproduction
Species Survival
Reproduction ensures the continuity and survival of species over time. It allows for the production of new individuals that can adapt to changing environments and challenges.
Genetic Diversity
Sexual reproduction introduces genetic diversity within populations, providing a reservoir of variations that can be subject to natural selection and evolution.
Adaptation and Evolution
Reproduction, particularly sexual reproduction, is a driving force in evolutionary processes. It allows for the accumulation of advantageous traits and the elimination of harmful ones over successive generations.
Population Dynamics
Reproduction influences population dynamics by regulating the size and distribution of populations. It plays a role in ecological balance and the interactions between species in ecosystems.
Life Cycle
Reproduction is often part of an organism’s life cycle, which includes stages such as growth, development, reproduction, and aging. The life cycle varies among different organisms.
Asexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction involves the production of offspring from a single parent without the involvement of gametes (sex cells) or the fusion of genetic material.
Sexual Reproduction
Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of gametes (sperm and egg) from two different parents, resulting in the formation of genetically diverse offspring.
Related Links
Asexual Reproduction
Embryo
Frond
Rhizome