Vertebrate
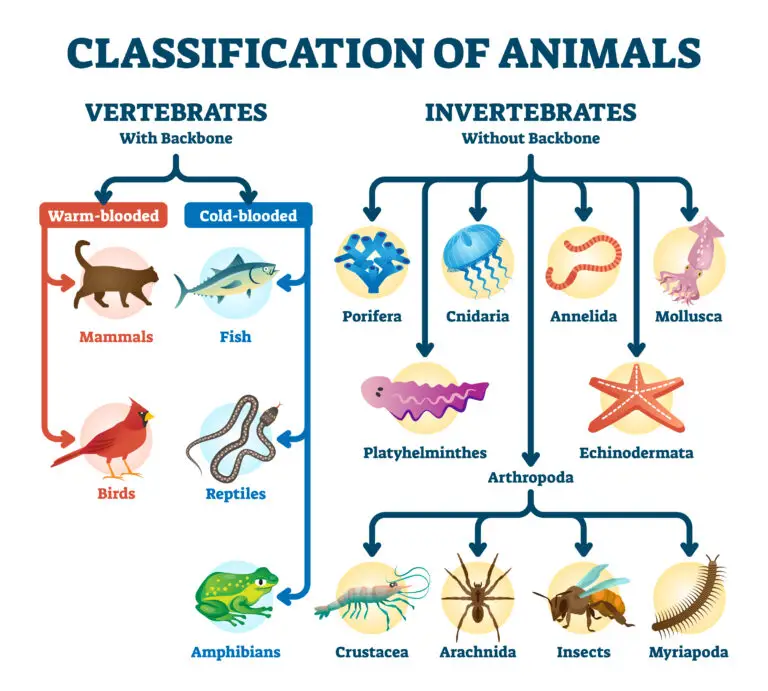
Table of Contents
What is a Vertebrate?
A vertebrate is an animal belonging to the subphylum Vertebrata, characterized by a vertebral column or backbone. Vertebrates comprise a diverse animal group, including mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fishes. The vertebral column, or spine, is a critical anatomical feature that provides structural support and protects the spinal cord.
Characteristics of Vertebrates
Vertebral Column
Vertebrates have a well-developed vertebral column composed of individual vertebrae. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, a crucial part of the central nervous system.
Internal Skeleton
Vertebrates have an internal skeleton made of bone or cartilage. This internal support system provides structure, protection, and anchorage for muscles.
Endoskeleton
The endoskeleton inside the body allows for flexibility and efficient movement. It also provides a framework for the attachment of muscles.
Well-Developed Nervous System
Vertebrates typically have a well-developed nervous system with a complex brain. The skull protects the brain, and the spinal cord runs through the vertebral column.
Closed Circulatory System
Vertebrates generally possess a closed circulatory system, where blood is confined to vessels and pumped by a heart. This allows for efficient transport of oxygen, nutrients, and waste products.
Complex Organ Systems
Vertebrates have well-developed organ systems, including digestive, circulatory, respiratory, and excretory systems.
Major Groups of Vertebrates
Mammals (Class Mammalia)
Mammals are characterized by features such as mammary glands, hair or fur, and a four-chambered heart. They give birth to live young and nurse them with milk. Examples include humans, dogs, and whales.
Birds (Class Aves)
Birds are characterized by feathers, a beak, and a lightweight skeleton with air sacs for efficient respiration. They lay eggs with hard shells. Examples include sparrows, eagles, and penguins.
Reptiles (Class Reptilia)
Reptiles have scales, lay amniotic eggs, and are often ectothermic (cold-blooded). Examples include snakes, turtles, and crocodiles.
Amphibians (Class Amphibia)
Amphibians typically have a moist skin, undergo metamorphosis, and are often found in both aquatic and terrestrial environments. Examples include frogs, salamanders, and newts.
Fishes (Superclass Pisces)
Fishes are aquatic vertebrates with scales and gills for respiration. There are various types of fishes, including bony fishes and cartilaginous fishes (sharks and rays).
Related Links
Bacteria
Homologous
Invertebrate
Kingdom