Evolution
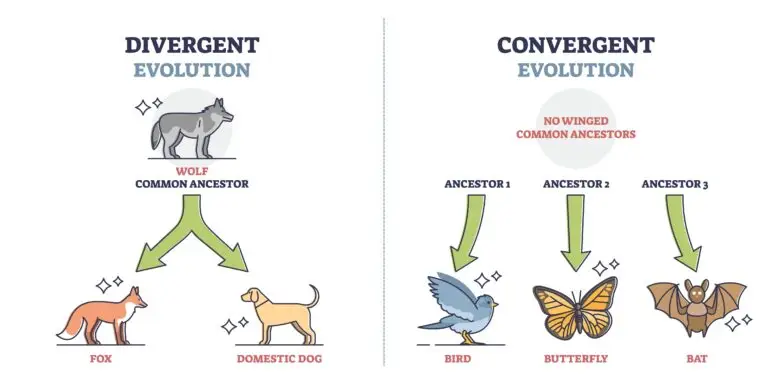
Table of Contents
Evolution in Biology
Evolution is the process of change in all forms of life over generations. It involves the descent of species from common ancestors and the development of new traits in populations over time.
As proposed by Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace, the theory of evolution provides a framework for understanding the mechanisms and patterns of evolutionary change.
Concepts of Evolution
Natural Selection
Natural selection is a mechanism of evolution where individuals with traits that confer advantages in a particular environment are more likely to survive and reproduce. Over time, the frequency of advantageous traits increases in a population.
Adaptation
Adaptation is how populations or species evolve traits that enhance their survival and reproductive success in a specific environment. Adaptations can be structural, behavioral, or physiological.
Genetic Variation
Genetic variation refers to the diversity in genetic material within a population or species. It is the result of differences in the DNA sequences of individuals, leading to variations in traits and characteristics.
Human Evolution
Human evolution is the evolutionary process that led to the emergence of Homo sapiens, the modern human species. It involves developing and adapting various hominid species over millions of years. The study of human evolution combines evidence from paleontology, genetics, anthropology, archaeology, and other disciplines.
Related Links
Adaptation
Biogenesis
Homologous
Natural Selection