Chromatid
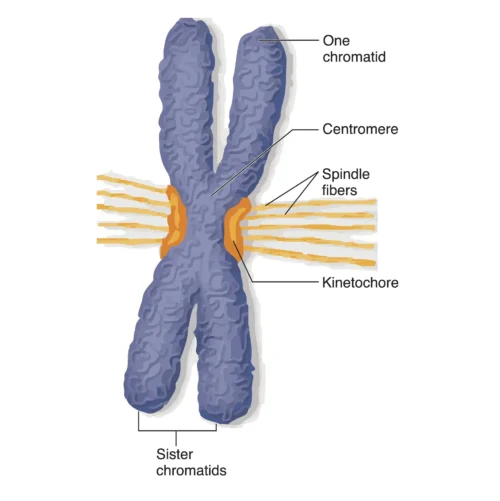
Table of Contents
What is a Chromatid?
A chromatid is one of the two identical copies of DNA that make up a duplicated chromosome connected by a centromere structure.
Chromatids are produced during the cell cycle’s S (synthesis) phase when DNA replication occurs. Each chromatid contains a complete set of genetic information and is considered a sister chromatid to the other one.
Chromatid Biology Basics
Formation
Chromatids are formed during the S phase of the cell cycle when a chromosome is replicated. Before replication, a chromosome consists of a single DNA molecule. After replication, the chromosome consists of two identical DNA molecules, each called a chromatid.
Centromere
The two chromatids of a duplicated chromosome are held together at a specific region called the centromere. The centromere plays a crucial role during cell division, as it is the point where the chromatids are attached and pulled apart.
Sister Chromatids
The two chromatids of a duplicated chromosome are held together at a specific region called the centromere. The centromere plays a crucial role during cell division, as it is the point where the chromatids are attached and pulled apart.
Mitosis and Meiosis
- Mitosis: During mitosis, chromatids are separated, and each sister chromatid is pulled to opposite poles of the dividing cell. This ensures that each daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes.
- Meiosis: Chromatids are also separated during meiosis, resulting in the formation of gametes (sperm or egg cells) with half the chromosome number.
Chromosome Number
Before DNA replication, a cell has a specific number of chromosomes. After replication, the number of chromatids doubles, but the chromosome number remains the same.
For example, if a cell has 6 chromosomes before replication, it will have 12 chromatids (6 pairs of sister chromatids) after replication.