Constant
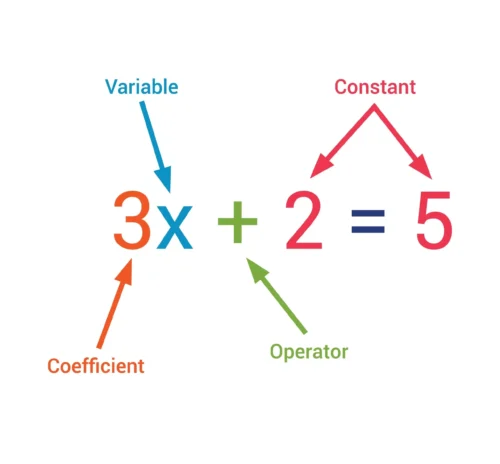
Table of Contents
What is a Constant?
A constant is a fixed numerical value that does not contain any variables. It is a term used to represent a specific, unchanging quantity in mathematical expressions or equations.
Examples of Constants
- 5, The number 5 is a constant. It does not change and has a fixed value.
- –3, Similarly, –3 is a constant. It is a specific, unchanging numerical value.
- \pi, The mathematical constant \pi (pi) represents the ratio of a circle’s circumference to its diameter and is approximately 3.14159.
- e, The mathematical constant e is the base of the natural logarithm and is approximately 2.71828.
- \frac{1}{2}, The fraction \frac{1}{2} is a constant, representing the numerical value of one-half.
Related Links
Arithmetic Sequence
Base (Algebra)
Coefficient
Equation