Consumer
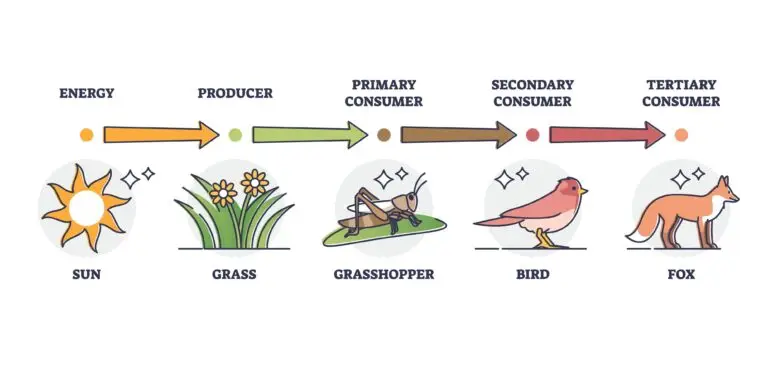
Table of Contents
Consumers in Biology
A consumer is an organism within an ecological food chain or food web that obtains its energy and nutrients by feeding on other organisms or organic matter. Consumers are heterotrophic organisms, meaning they cannot produce their own food and must rely on external sources for nutrition.
Consumers play a vital role in energy transfer within ecosystems as they participate in the consumption and processing of organic matter produced by autotrophic organisms.
Key Roles of Consumers
Types of Consumers
- Primary Consumers (Herbivores): These consumers feed directly on plants or autotrophic organisms. They are the first level of consumers in a food chain.
- Secondary Consumers (Carnivores): These consumers feed on primary consumers. They are typically carnivores that consume herbivores.
- Tertiary Consumers (Carnivores): These consumers feed on secondary consumers. They are carnivores that consume other carnivores.
- Omnivores: Omnivores are consumers that feed on both plants (or other autotrophs) and animals. Humans are examples of omnivores.
Energy Transfer
Consumers play a crucial role in the transfer of energy within ecosystems. They obtain energy by consuming other organisms, which, in turn, have obtained their energy from the sun through photosynthesis (in the case of autotrophs).
Food Chain and Food Web
- A food chain is a linear sequence that represents the flow of energy from one trophic level to another. It typically starts with primary producers (plants) and progresses through primary consumers, secondary consumers, and so on.
- A food web is a more complex representation of feeding relationships in an ecosystem. It includes interconnected food chains and accounts for the multiple ways in which organisms interact.
Detritivores and Decomposers
- Detritivores: Some consumers feed on dead organic matter (detritus). These organisms are called detritivores, and they play a role in breaking down and recycling organic material.
- Decomposers: Decomposers, such as bacteria and fungi, further break down organic matter into simpler substances, returning nutrients to the environment.
Role in Ecosystems
Consumers help regulate populations of other organisms within ecosystems through predation and herbivory. They contribute to nutrient cycling as they consume and release nutrients back into the environment through waste.
Related Links
Food Chain
Herbivore
Heterotroph
Omnivore