Decomposer
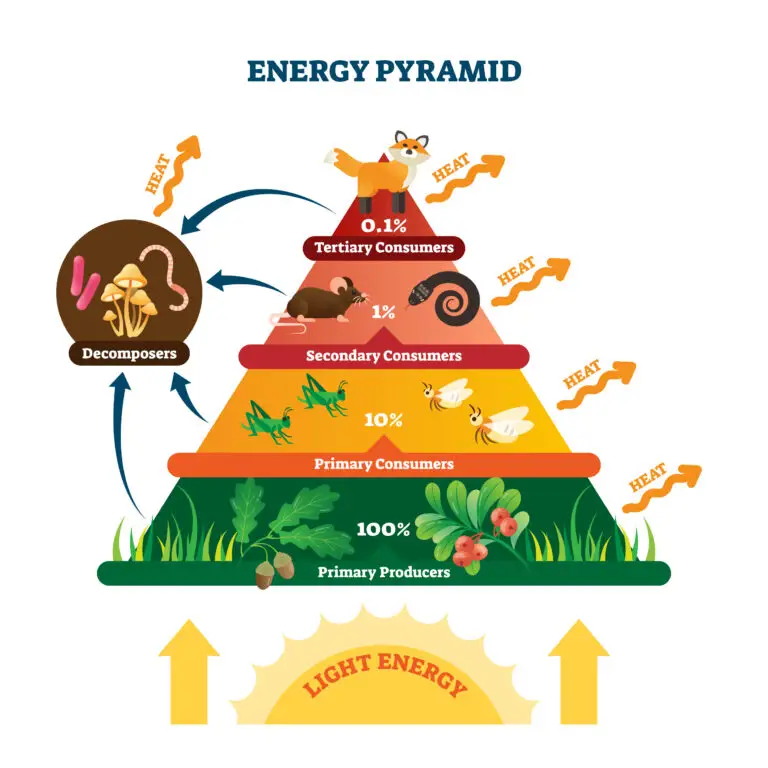
Table of Contents
Decomposer in Bology
In biology, a decomposer is an organism that plays a crucial role in breaking down and decomposing dead organic matter, including the remains of plants and animals.
Decomposers are essential to the nutrient cycling process within ecosystems. They contribute to the breakdown of complex organic substances into simpler compounds. These simpler compounds are then recycled back into the environment, making them available for use by other living organisms.
Overview of Decomposers
Function
Decomposers function as nature’s recyclers, breaking down complex organic material into simpler forms. They play a vital role in the decomposition of dead organisms, fallen leaves, and other organic debris.
Types of Decomposers
- Bacteria: Many bacteria are decomposers and are involved in the decomposition of organic matter. They break down complex molecules into simpler compounds through biochemical processes.
- Fungi: Fungi, such as molds and mushrooms, are efficient decomposers. They secrete enzymes that break down organic material externally, and the resulting simpler compounds are then absorbed by the fungi.
- Detritivores: Organisms such as earthworms, insects, and certain crustaceans are detritivores that physically break down organic matter into smaller particles. They facilitate the decomposition process and contribute to soil aeration.
Decomposition Process
Decomposers release enzymes that break down complex organic molecules (such as carbohydrates, proteins, and fats) into simpler compounds. The decomposition process involves the conversion of organic material into substances like carbon dioxide, water, minerals, and organic nutrients.
Nutrient Recycling
Decomposers play a crucial role in nutrient cycling by releasing essential nutrients (such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and carbon) back into the ecosystem. The recycled nutrients become available to plants and other organisms, completing the cycle of nutrient flow within an ecosystem.
Detoxification
Decomposers also contribute to the detoxification of the environment by breaking down harmful substances and organic pollutants.
Related Links
Consumer
Ecosystem
Food Chain
Trophic Level