DNA
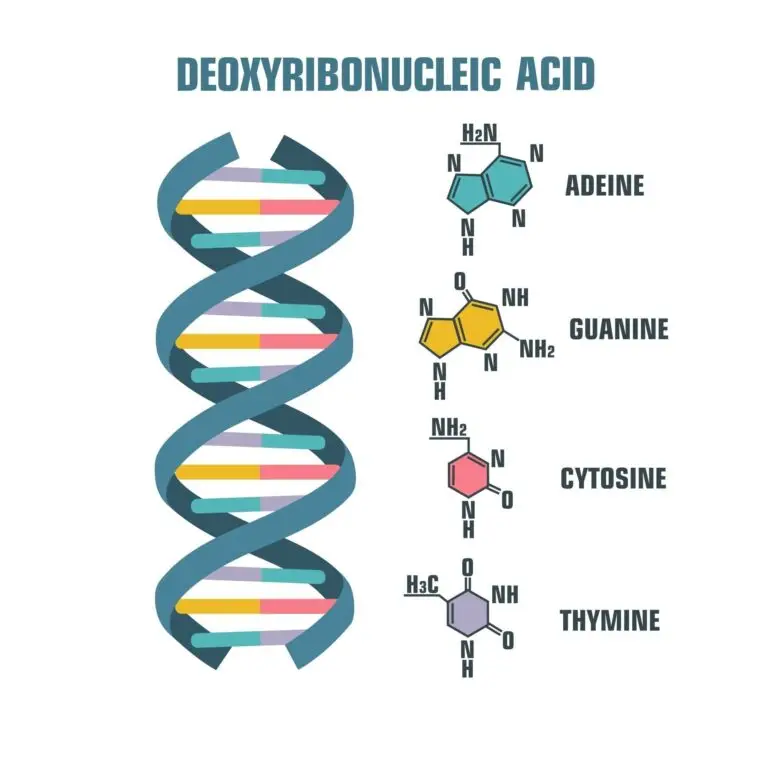
Table of Contents
What is DNA?
DNA, or Deoxyribonucleic Acid, is a molecule that carries the genetic instructions used in the development, functioning, growth, and reproduction of all known living organisms. It is a type of nucleic acid and plays a fundamental role in storing and transmitting genetic information.
DNA Structure
Double Helix
- DNA has a distinctive double-helix structure, resembling a twisted ladder.
- The two sides of the ladder are formed by alternating sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate molecules, forming the “backbone” of the DNA molecule.
Nucleotide Base Pairs
The rungs of the DNA ladder are formed by pairs of nucleotide bases. There are four types of bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G).
Adenine always pairs with thymine, and cytosine always pairs with guanine, creating complementary base pairs.
Base Pairing Rules
- Adenine (A) pairs with Thymine (T) through two hydrogen bonds.
- Thymine (T) pairs with Adenine (A) through two hydrogen bonds.
- Cytosine (C) pairs with Guanine (G) through three hydrogen bonds.
- Guanine (G) pairs with Cytosine (C) through three hydrogen bonds.
Genes
DNA houses genes, distinct sequences of nucleotides responsible for coding proteins or functional RNA molecules. These genes serve as the instructions for protein synthesis, playing a critical role in determining an organism’s physical and functional traits.
Proteins, synthesized according to the genetic code, are crucial for the structure, regulation, and operation of the body’s cells, tissues, and organs. They perform many functions, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, replicating DNA, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules.
DNA Replication
DNA replication is the process by which DNA makes an identical copy of itself during cell division. The two strands of the double helix separate, and each strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary strand
Role in Inheritance
- DNA is the hereditary material, and the sequence of nucleotide bases in DNA determines an organism’s traits and characteristics.
- During sexual reproduction, offspring inherit a combination of DNA from both parents, contributing to genetic diversity.
Related Links
Atom
Asexual Reproduction
Bioinformatics
Cloning