Exponent
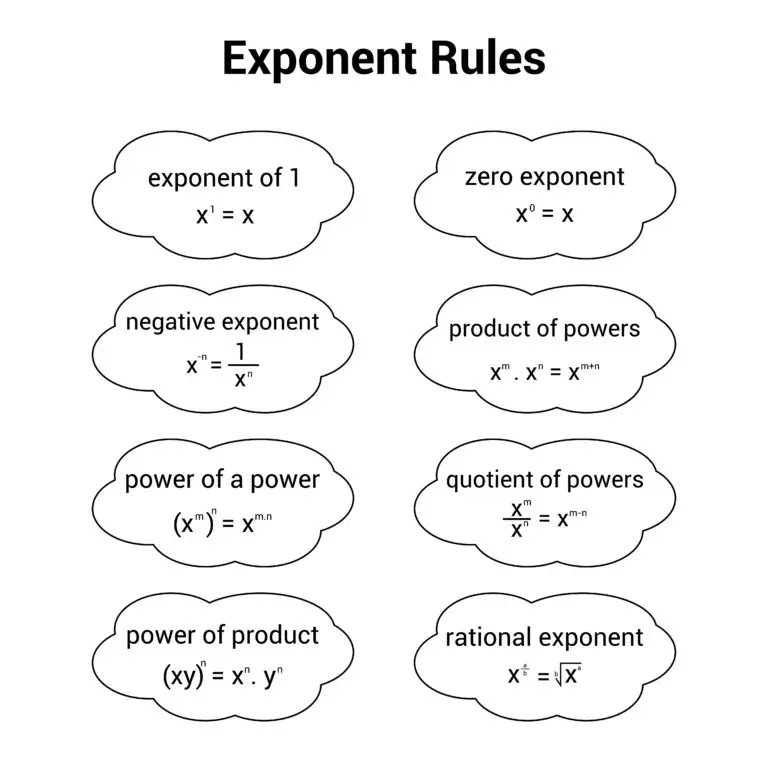
Table of Contents
Exponents in Algebra
In algebra, an exponent is a mathematical notation representing the number of times a base is multiplied by itself. A small raised number denotes the exponent to the right of the base. It indicates the power to which the base is raised.
If a is the base and n is the exponent, the expression is written as a^n, where a is multiplied by itself n times.
Examples of Exponents
- 2^3 means 2 raised to the power of 3, which is 2\times2\times2=8.
- 5^2 means 5 raised to the power of 2, which is 5\times5=25.
- 3^4 means 3 raised to the power of 4, which is 3\times3\times3\times3=81.
- 10^0 means 10 raised to the power of 0, which is always 1 (any nonzero number raised to the power of 0 is 1).
- x^2 means x raised to the power of 2, which is x^x.
Related Links
Binomial
Conjugate Pair
Monomial
Term