Expression
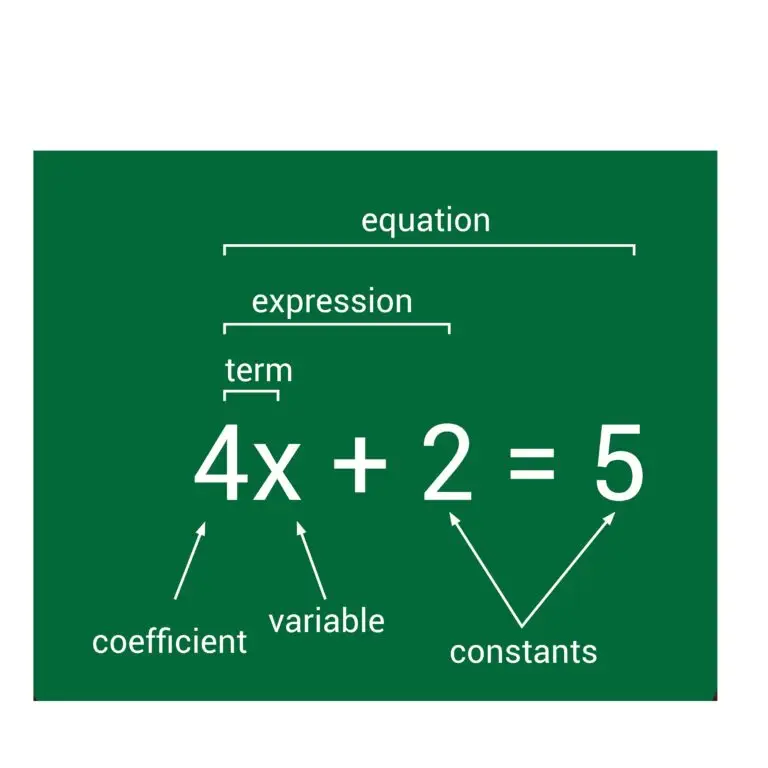
Table of Contents
Algebraic Expressions
An expression is a mathematical phrase representing a combination of numbers, variables, operations, and symbols. Expressions can be simple, like a single variable, constant, or complex, involving multiple terms and operations.
Expressions can be simplified, factored, or expanded using various algebraic techniques. They are the building blocks of algebraic equations and inequalities, providing a way to represent mathematical relationships in a concise form.
Components of an Expression
Variables: Symbols that represent unknown or varying values, often denoted by letters such as x, y, or a.
Constants: Specific numerical values that do not change, such as 2, \pi, or –5.
Coefficients: Numerical factors that multiply variables, like the 3 in 3x.
Operations: Mathematical operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and exponentiation that combine terms within the expression.
Parentheses and Brackets: Used to indicate the order of operations and grouping.
Examples
Simple Expression: x+5, This expression involves the variable x and the constant 5.
Linear Expression: 3x-2y+7, A linear expression with terms involving variables (x and y) and constants.
Quadratic Expression: 2x^2-4x+1, A quadratic expression with a variable (x) raised to the power of 2.
Fractional Expression: \frac{2}{3}x-\frac{5}{2}, An expression with fractional coefficients.
Complex Expression: (x+3)(2y-5), An expression involving parentheses, indicating multiplication of binomials.
Related Links
Coefficient
The Art of Factoring
Inequality
Term