Factor
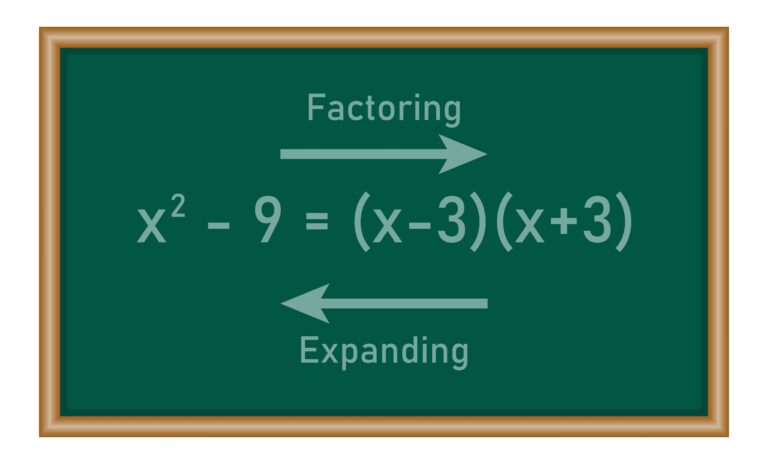
Table of Contents
Factors in Math
A factor of an expression is a quantity that divides the expression without leaving a remainder. Factoring refers to expressing a mathematical expression as a product of its factors. Factors are always positive whole numbers.
Factoring is an essential skill in algebra, often used to simplify expressions, solve equations, and understand the structure of mathematical relationships.
Examples of Factoring
Factoring a Constant: 6=2\times3, Here, 2 and 3 are factors of 6. Factoring 6 involves expressing it as a product of its prime factors.
Factoring a Linear Expression: x+5, This expression can be factored by taking out the common factor, which is 1 in this case. x+5=1\times(x+5)
Factoring a Quadratic Expression: x^2-4x+4, This quadratic expression can be factored as (x-2)(x-2)\text{ or }(x-2)^2.
Factoring by Grouping: xy+3x+2y+6, Grouping the terms allows for factoring by common factors: (xy+3x)+(2y+6)=x(y+3)+2(y+3)=(x+2)(y+3)
Factoring a Difference of Squares: a^2-b^2, This expression can be factored as (a-b)(a+b).
Factoring a Trinomial: x^2+5x+6, This trinomial can be factored as (x+2)(x+3).
Related Links
Cross-Multiplication
Like Terms
Polynomial
The Art of Factoring