Function
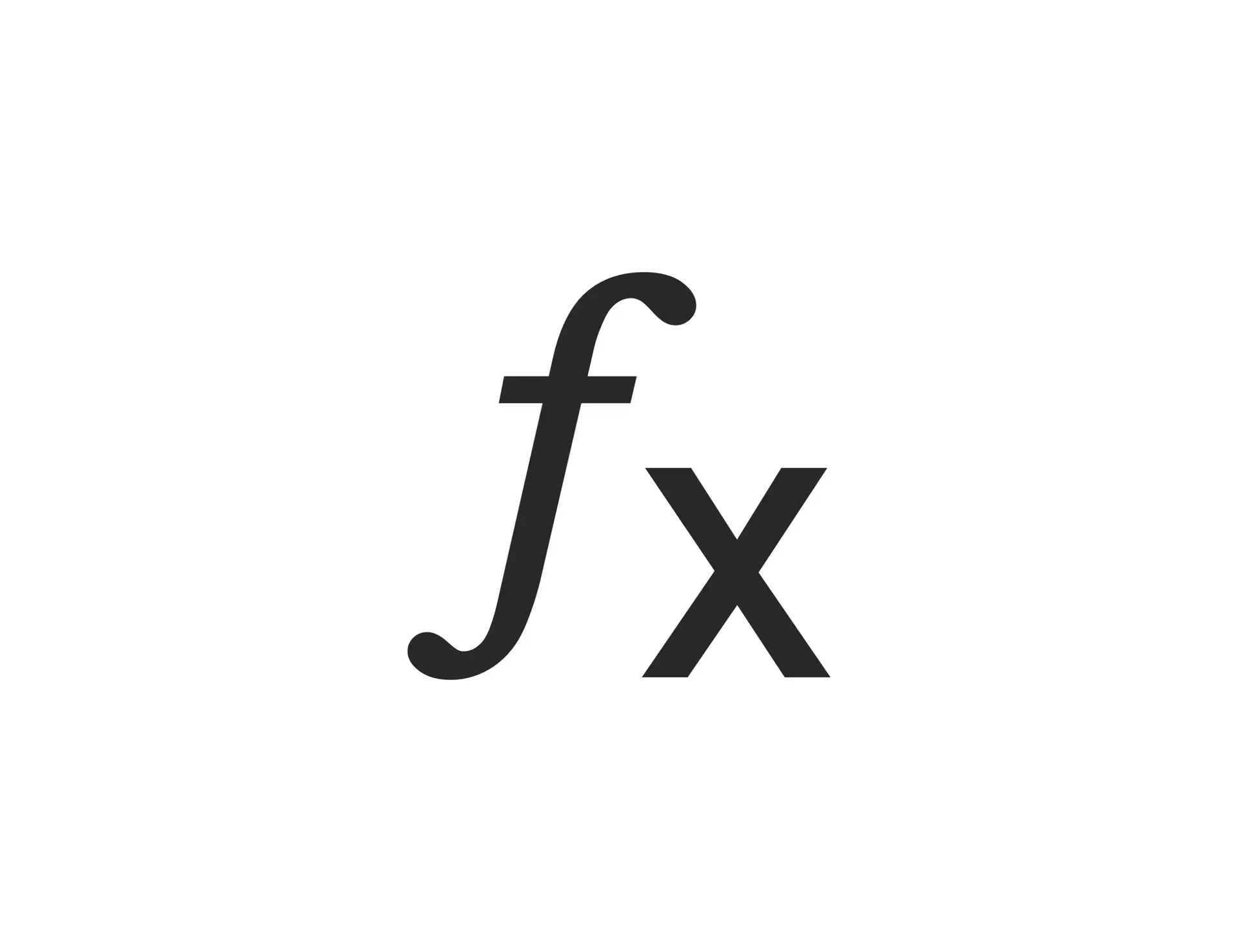
Table of Contents
Math Functions
A function is a relation between two sets of numbers, where each element in the first set (called the domain) is paired with exactly one element in the second set (called the codomain).
The key characteristic of a function is that each input (element in the domain) corresponds to a unique output (element in the codomain).
A function is often denoted by a rule that describes how the input values are related to the output values. If f is a function, the notation f(x) represents the output associated with the input x.
Components of Functions
- Domain: The set of input values for which the function is defined.
- Codomain: The set of possible output values.
- Mapping: The association between each element in the domain and its corresponding element in the codomain.
Function Examples
Linear Function: f(x)=2x+3, In this linear function, for each value of x, the corresponding output is obtained by multiplying x by 2 and adding 3.
Quadratic Function: g(x)=x^2-4, The quadratic function g(x) assigns to each x the value obtained by squaring x and subtracting 4.
Absolute Value Function: h(x)=|x|, The absolute value function h(x) assigns to each x the non-negative value of x.
Related Links
Absolute Error
Arithmetic Mean
Rational Number
Variable