Gamete
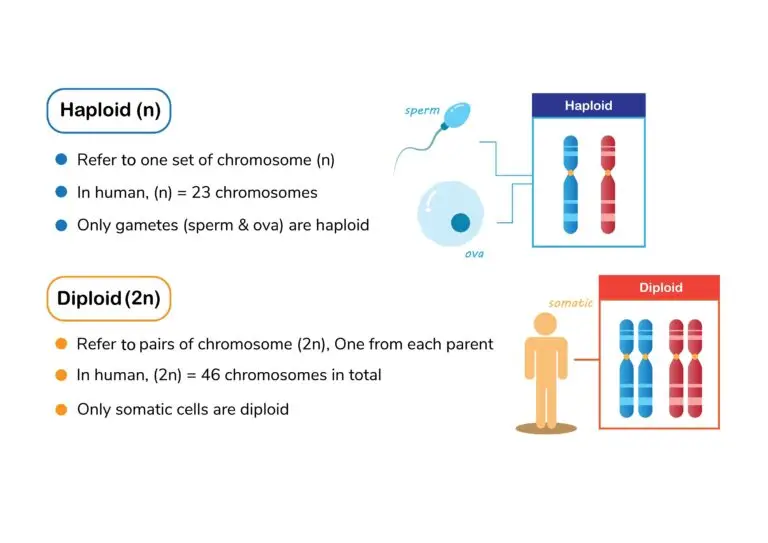
Table of Contents
What is a Gamete?
A gamete is a specialized reproductive cell that fuses with another gamete during sexual reproduction to form a zygote. Gametes are essential for transmitting genetic material from one generation to the next. In sexually reproducing organisms, there are two types of gametes: male gametes (sperm) and female gametes (eggs or ova).
Gametes in Reproduction
Haploid Cells
Gametes are haploid cells, meaning they contain half the number of chromosomes found in an organism’s somatic (body) cells. In humans, for example, somatic cells are diploid (2n), while gametes are haploid (n).
Meiosis
The process of gamete formation involves meiosis, a type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half. Meiosis includes two divisions (meiosis I and meiosis II), producing four haploid cells, each with a unique combination of genetic material.
Male Gametes (Sperm)
In males, the gametes are called sperm. Sperm cells are typically small, motile, and adapted for swimming to reach and fertilize the egg. They are produced in the testes through spermatogenesis.
Female Gametes (Eggs or Ova)
In females, the gametes are called eggs or ova. Eggs are larger and non-motile compared to sperm. They are produced in the ovaries through oogenesis. In some organisms, including humans, only one functional egg is produced during each reproductive cycle.
Gonads
Gametogenesis occurs in specialized reproductive organs called gonads. In males, the gonads are the testes, while in females, they are the ovaries.
Germ Cells
Gametes are considered germ cells because they give rise to the next generation of organisms. The genetic information they carry is passed on to offspring during fertilization.
Related Links
Asexual Reproduction
Metaphase
Prophase
Telophase