Gene
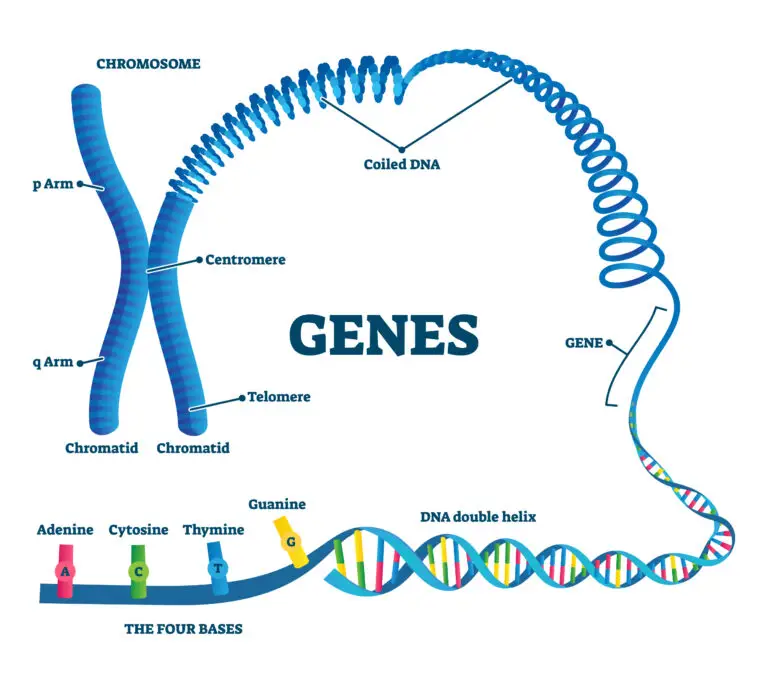
Table of Contents
What is a Gene?
A gene is a DNA segment containing instructions for building and maintaining one or more functional molecules, usually proteins or RNA molecules. Genes are the fundamental units of heredity, carrying the genetic information that determines an organism’s traits and characteristics.
DNA as the Genetic Material
Genes are composed of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), a long, double-stranded molecule with a unique sequence of nucleotide bases. The sequence of these bases (adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine) in a gene encodes the genetic code.
Genetic Code and Proteins
The information stored in genes is transcribed into RNA through transcription. The RNA serves as a template for translation, where amino acids are assembled into proteins based on the genetic code.
Proteins and Function
- Genes play a crucial role in determining an organism’s traits by specifying the synthesis of proteins.
- Proteins are essential for the structure and function of cells, tissues, and organs.
Functional RNA Molecules
Not all genes code for proteins. Some genes produce functional RNA molecules, such as ribosomal RNA (rRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), and microRNA (miRNA). These RNA molecules have various roles in cellular processes, including protein synthesis and gene regulation.
Alleles
Different versions or variants of a gene are called alleles. Alleles may result from mutations, and they can influence the expression of traits in an organism.
Genome
An organism’s complete set of genes is known as its genome. Genomes can vary in size and complexity among different species.
Genetic Variation
Genetic variation within populations arises from differences in gene sequences, contributing to the diversity of traits in a species. Genetic variation is essential for evolution and adaptation.
Related Links
Genetic Code
Genotype
Karyotype
Prophase