Genotype
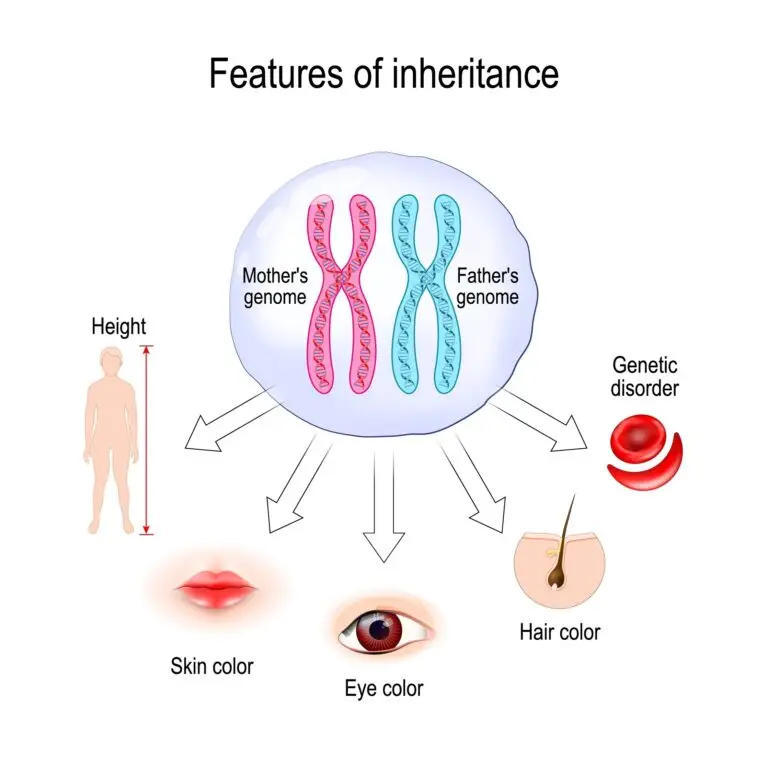
Table of Contents
What is a Genotype?
Genotype refers to the genetic makeup of an organism, which includes the specific set of genes (alleles) present in its DNA. It determines the genetic information that an organism inherits from its parents and influences its traits, characteristics, and potential for variations in phenotype (observable traits).
Genotype in Genetics
Genetic Information
The genotype represents the complete set of genes carried by an individual. It includes both the alleles inherited from each parent for each gene.
Alleles
Genes exist in multiple forms known as alleles. The genotype specifies which alleles an individual possesses for each gene. For example, if a gene has two possible alleles (A and a), an individual’s genetic mackup could be AA, Aa, or aa.
Homozygous and Heterozygous Genotypes
- Homozygous: occurs when an individual has two identical alleles for a specific gene (e.g., AA or aa).
- Heterozygous: occurs when an individual has two alleles for a gene (e.g., Aa).
Diploid Organisms
In diploid organisms like humans, the genotype consists of pairs of chromosomes, with each parent contributing one chromosome to each pair. Each chromosome carries genes, and the combination of alleles on the paired chromosomes determines the genotype.
Genotype Inheritance
The genetic information of an organism is inherited from parents during sexual reproduction. Offspring inherit one set of chromosomes from each parent, resulting in a combination of alleles contributing to their genetic makeup.
Genetic Disorders
Some genotypes may carry alleles associated with genetic disorders or conditions. Understanding this genetic information can be important for predicting the likelihood of certain traits or conditions in individuals or their offspring.
Related Links
Allele
Dominant Traits
Genome
Karyotype