Imaginary Unit
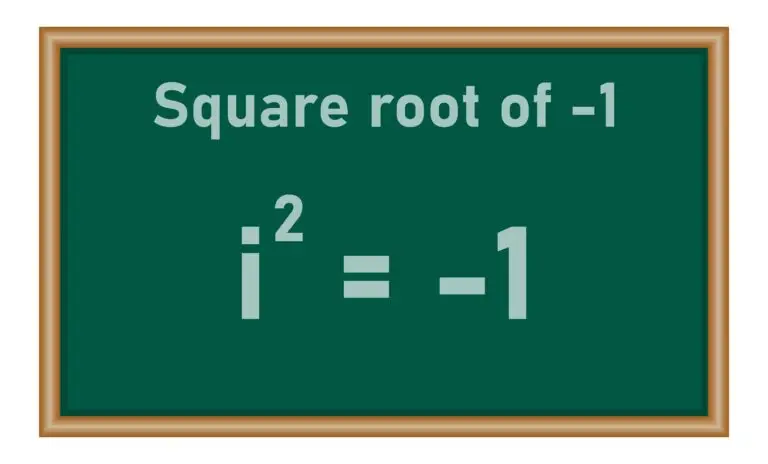
Table of Contents
What is an Imaginary Unit?
An imaginary unit in algebra is a mathematical concept denoted by the symbol i, representing the square root of -1. It is used to extend the number system to include complex numbers, which are numbers in the form a+bi, where a and b are real numbers and i is the imaginary unit.
Mathematically, i^2=\text{-}1. The concept of the imaginary unit is essential in the field of complex numbers, where numbers of the form a+bi include a real part (a) and an imaginary part (bi).
Complex numbers allow for the representation of quantities beyond the real number line.
Imaginary Unit Explanation
- i is an imaginary unit, and i^2=\text{-}1.
- Complex numbers are written in the form a+bi, where a and b are real numbers.
- The real part of the complex number a+bi is a, and the imaginary part is bi.
- Imaginary numbers are multiples of the imaginary unit, such as 2i or –3i.
Imaginary Unit Examples
Basic Imaginary Numbers
- i
- 2i
- –3i
Complex Numbers
- 3+4i
- –2-i
- –1-2i
Operations with Imaginary Units
- i\times i=i^2=-1
- (3+2i)+(1-5i)=4-3i
- (2-i)(3+2i)=6+4i-3i-2^i=8+i-2(-1)=10+i
Related Links
Complex Number
Conjugate Pair
Like Terms
Monomial