Inequality
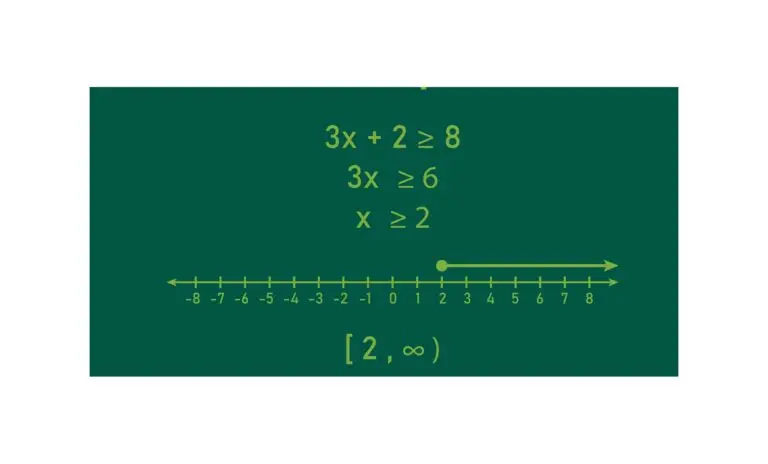
Table of Contents
What is an Inequality?
Inequality is a mathematical statement that expresses a relationship between two expressions, typically denoted by one of the inequality symbols: < (less than), > (greater than), \le (less than or equal to), \ge (greater than or equal to), or \ne (not equal to).
An inequality indicates that one expression has a certain relationship with another, such as being smaller, greater, or not equal.
Notation
- a<b means a is less than b.
- a>b means a is greater than b.
- a\le b means a is less than or equal to b.
- a\ge b means a is greater than or equal to b.
- a\ne b means ais not equal to b.
Examples of Inequalities
Strict Inequality: x<5, This inequality states that x is less than 5, but not equal to 5.
Non-strict Inequality: y\ge \text{-}2, This inequality states that y is greater than or equal to –2.
Compound Inequality: \text{-}3<z\le 1, This compound inequality combines two inequalities and indicates that z is greater than –3 and less than or equal to 1.
Absolute Value Inequality: |x-4|< 3, This inequality involves the absolute value and states that the distance between x and 4 is less than 3.
Inequality with Variables: 2y+7\ge 13, This inequality involves a variable y and states that 2y+7 is greater than or equal to 13.
Related Links
Base (Algebra)
Binomial
Constant
Factors