Inheritance
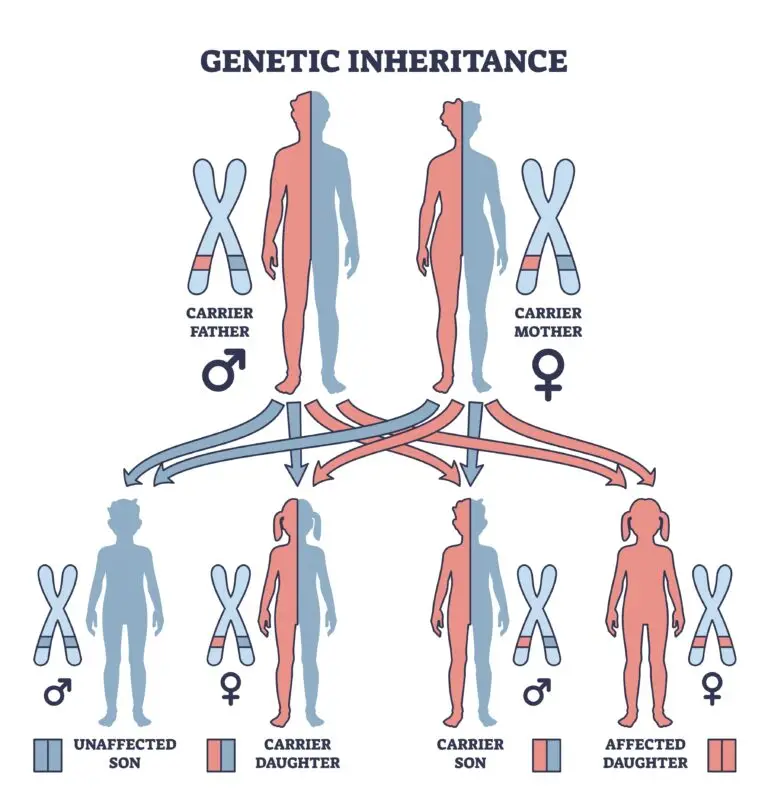
Table of Contents
What is Inheritance?
Inheritance refers to passing genetic information from one generation to the next. It involves the transmission of traits, characteristics, and genetic material (DNA) from parent organisms to their offspring.
The study of inheritance is a key aspect of genetics, which explores the principles and mechanisms underlying the passage of genetic information and the variation observed among individuals.
Understanding Inheritance in Biology
Genes
Genes are segments of DNA that code for specific traits or characteristics. They serve as the units of heredity and are located on chromosomes within the cell’s nucleus.
Chromosomes
Chromosomes are structures composed of DNA and proteins that carry genes. In sexually reproducing organisms, chromosomes are found in pairs (one from each parent).
Diploid and Haploid Cells
Organisms with a diploid life cycle have cells containing two sets of chromosomes (one from each parent), while haploid cells have only one set of chromosomes. Gametes (sperm and egg cells) are examples of haploid cells.
Meiosis
Meiosis is the process of cell division that produces gametes. During meiosis, the chromosome number is halved, resulting in the formation of haploid cells. When gametes fuse during fertilization, the zygote’s diploid chromosome number is restored.
Dominant and Recessive Traits
Some alleles are dominant, expressing their traits in the presence of another allele. Recessive alleles are expressed only when both alleles in a pair are recessive. This leads to the expression of dominant traits in heterozygous individuals.
Mendelian Inheritance
Based on Gregor Mendel’s work, Mendelian inheritance describes the inheritance patterns for single-gene traits. Mendel’s laws include the law of segregation and the law of independent assortment.
Polygenic Inheritance
Many traits are influenced by multiple genes and exhibit polygenic inheritance. These traits often show a range of phenotypes, contributing to continuous variation.
Epigenetics
Epigenetic factors, such as DNA methylation and histone modification, can influence gene expression and inheritance. Epigenetic modifications can be passed from generation to generation and play a role in development and disease.
Related Links
Overview of DNA
Dominant Traits
Genetic Variation
Genotype