Kingdom
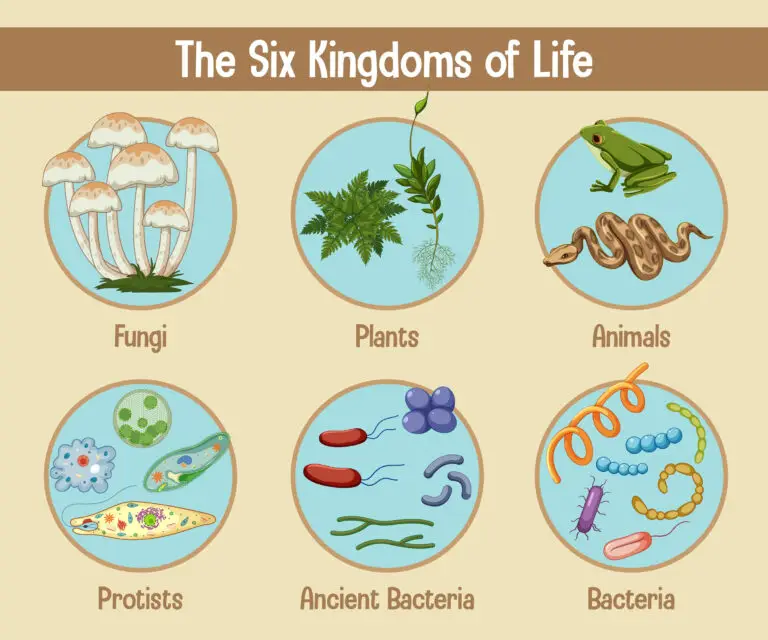
Table of Contents
Kingdom Classification
A kingdom is a taxonomic rank that is one of the highest levels of classification in the hierarchy of life. Organisms are grouped into different kingdoms based on fundamental characteristics such as cellular structure, mode of nutrition, and overall organization. The concept of kingdoms is part of the broader system of taxonomy, which is the science of naming, defining, and classifying living organisms.
Five Major Kingdoms
Animalia (Animal Kingdom)
Organisms in this kingdom are multicellular, eukaryotic (having cells with a nucleus), and primarily heterotrophic (obtaining nutrients by consuming other organisms). Animals display a wide variety of body plans and modes of locomotion.
Plantae (Plant Kingdom)
Members of the plant kingdom are multicellular, eukaryotic, and autotrophic (synthesize their own food through photosynthesis). Plants are characterized by cell walls containing cellulose and the presence of chloroplasts.
Fungi (Fungus Kingdom)
Fungi are eukaryotic, primarily multicellular, and heterotrophic organisms that obtain nutrients through absorption. They often form structures such as mycelium and reproduce by producing spores.
Protista (Protist Kingdom)
The kingdom Protista includes diverse and mostly unicellular eukaryotic organisms. Protists do not fit neatly into the categories of animals, plants, or fungi. Some are autotrophic, while others are heterotrophic.
Monera (Bacteria Kingdom)
The kingdom Monera includes prokaryotic organisms, specifically bacteria. Bacteria are unicellular, lack a true nucleus, and have a simpler cellular organization compared to eukaryotes. They can be found in various environments and play essential roles in ecosystems.
Related Links
Carnivore
Genus
Taxonomy
Vertebrate