Louisiana Purchase
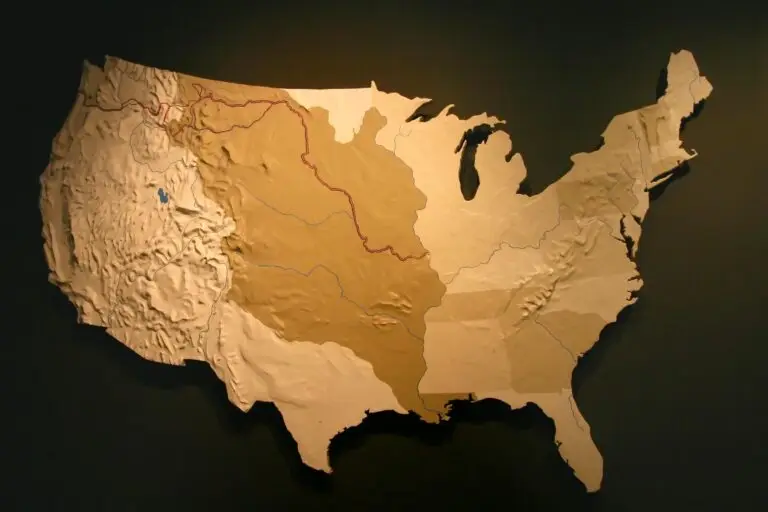
Table of Contents
What is the Louiana Purchase?
The Louisiana Purchase refers to the acquisition of a vast territory in North America by the United States from France in 1803. The purchase doubled the size of the young nation, profoundly influencing its geography, politics, and expansion.
Lousiana Purchase History
The Louisiana Purchase was a land deal between the United States and France, where the U.S. acquired approximately 828,000 square miles of territory west of the Mississippi River in 1803.
The territory acquired in the Louisiana Purchase included parts or all of 15 present-day states, stretching from the Mississippi River to the Rocky Mountains.
The negotiations for the Louisiana Purchase were led by U.S. representatives James Monroe and Robert R. Livingston and French diplomat François Barbe-Marbois.
The purchase price for the Louisiana Territory was $15 million, which equated to roughly four cents per acre, making it one of the most economically advantageous land deals in history.
The decision to pursue the Louisiana Purchase was driven by President Thomas Jefferson’s desire to secure access to the port of New Orleans and the Mississippi River for American trade.
Napoleon Bonaparte, facing challenges in Haiti and the looming threat of war with Britain, decided to sell the Louisiana Territory to the United States, abandoning his plans for a French empire in North America.
The Louisiana Purchase doubled the size of the United States and had profound implications for westward expansion and the future development of the nation.
The Lewis and Clark Expedition, led by Meriwether Lewis and William Clark, was commissioned by President Jefferson to explore the newly acquired territory, document its resources, and establish an American presence.
The Louisiana Purchase was officially ratified on October 20, 1803, and the transfer of authority took place in St. Louis on March 10, 1804.
The acquisition of the Louisiana Territory set a precedent for future territorial expansion and negotiations, shaping the geographic and economic landscape of the United States in the 19th century.
Related Links
The American Revolution
Industrial Revolution
Roe v. Wade
Louisiana Purchase