Lysosome
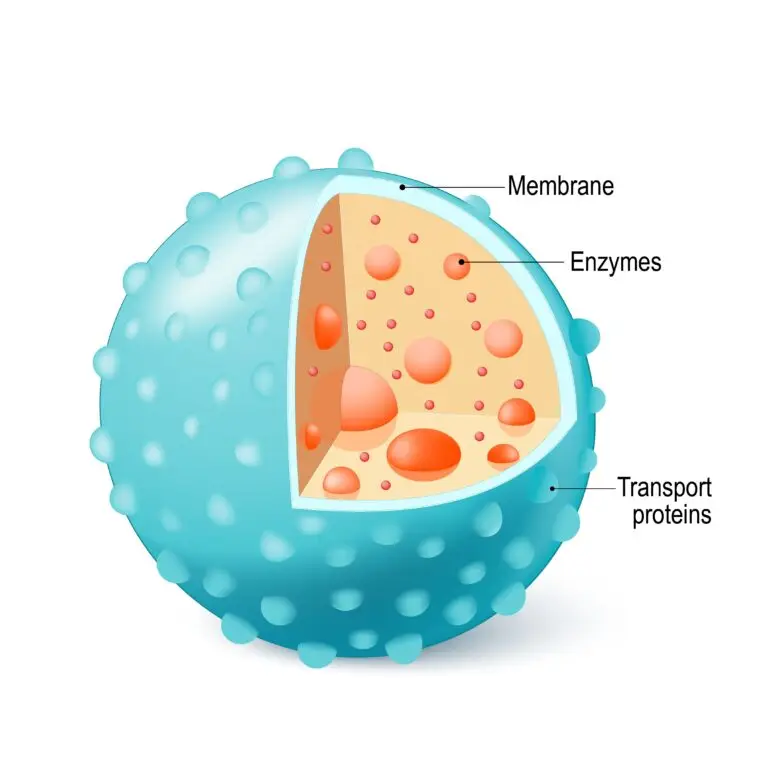
Table of Contents
What is Lysosome?
A lysosome is a membrane-bound organelle found in the cells of animals, plants, fungi, and protists. It is known as the cell’s “garbage disposal” or “recycling center” because its primary function is to break down and digest cellular waste materials, macromolecules, and foreign substances.
They contain a variety of enzymes that work together to break down complex molecules into simpler components that can be recycled or eliminated.
Functions of Lysosomes
Membrane Structure
Lysosomes are membrane-bound vesicles with an acidic interior. The membrane of the lysosome isolates the digestive enzymes from the rest of the cell, preventing them from causing damage to other cellular components.
Enzyme Composition
Lysosomes contain a variety of hydrolytic enzymes, including proteases (for breaking down proteins), lipases (for breaking down lipids), nucleases (for breaking down nucleic acids), and glycosidases (for breaking down carbohydrates). These enzymes are active at low pH, creating an acidic environment within the lysosome.
Endocytosis and Phagocytosis
Lysosomes are involved in the process of endocytosis, where cells engulf particles from the extracellular environment by forming vesicles. Phagocytosis, a specialized form of endocytosis, involves the engulfment of large particles, such as bacteria, which are then delivered to lysosomes for digestion.
Digestion of Cellular Components
Lysosomes break down cellular components such as worn-out organelles, malfunctioning mitochondria, and other cellular debris. This process contributes to the renewal and maintenance of cellular structures.
Role in Cell Death
Lysosomes are involved in programmed cell death (apoptosis). During apoptosis, lysosomes release enzymes that contribute to the breakdown of cellular components, facilitating the orderly removal of dying cells.
Related Links
Digestion
Excretion
Organelle
Vesicle