Mitosis
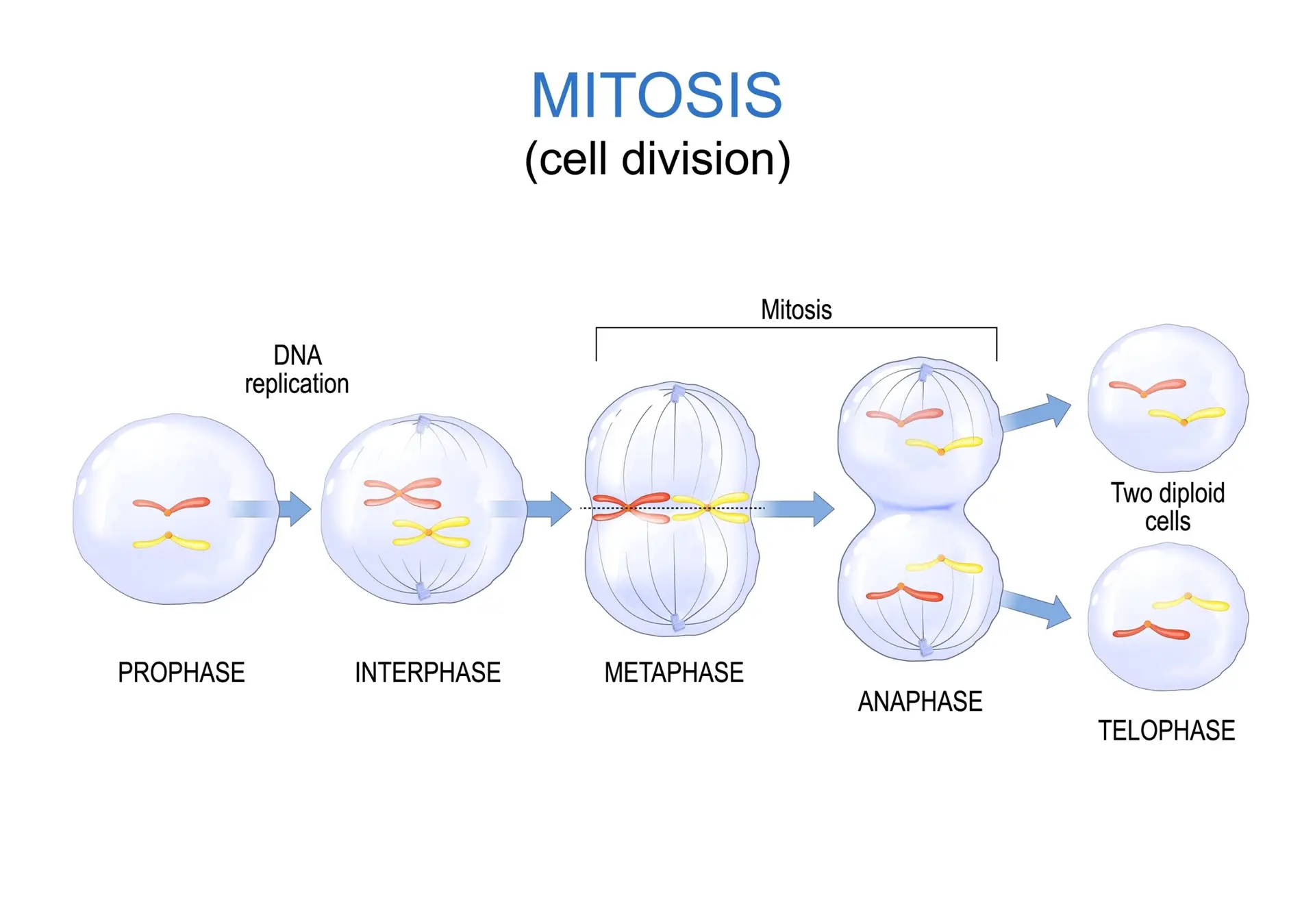
Table of Contents
Definition of Mitosis
Mitosis is a process of cell division that results in the formation of two genetically identical daughter cells, each having the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
This type of cell division is essential for growth, development, tissue repair, and asexual reproduction in eukaryotic organisms. Mitosis ensures that the genetic material is faithfully distributed to daughter cells, maintaining the stability of the organism’s genome.
Features of Mitosis
Chromosome Conservation
Mitosis maintains the diploid chromosome number in daughter cells, ensuring that each cell has the same genetic information as the parent cell.
Single Division
Mitosis involves a single division of the cell’s nucleus, resulting in the formation of two daughter nuclei.
Four Stage
Mitosis consists of four main stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
- During prophase, chromosomes condense, the nuclear envelope breaks down, and the mitotic spindle forms.
- Metaphase involves the alignment of chromosomes at the cell’s equator.
- In anaphase, sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles.
- Telophase marks the end of mitosis, with the reformation of nuclear envelopes around the separated chromatids.
Growth and Tissue Repair
Mitosis is critical for the growth and development of multicellular organisms. It is also important for the replacement of damaged or dead cells in tissues.
Asexual Reproduction
Some unicellular and simple multicellular organisms use mitosis as a form of asexual reproduction, producing offspring that are genetically identical to the parent.
Related Links
Asexual Reproduction
Cloning
Prophase
Telophase