Nervous System
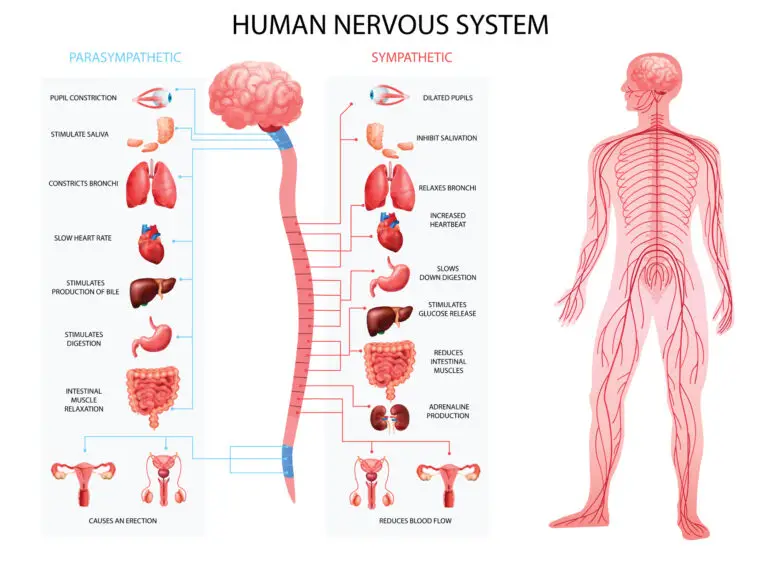
Table of Contents
What is the Nervous System?
The nervous system is a complex network of specialized cells, tissues, and organs that coordinate and control various functions throughout the body. It is responsible for the transmission of signals between different parts of the body, allowing organisms to respond to their environment, process information, and regulate internal processes.
The nervous system can be divided into two main components: the Central Nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Functions of the Nervous System
Sensory Reception
The nervous system actively gathers information about the surrounding environment and the internal conditions of the body using sensory receptors. These receptors detect various stimuli, such as light, sound, temperature, and pressure, and convert them into electrical signals that are sent to the brain for processing. This process allows organisms to perceive and respond to changes in their external and internal environments, facilitating interaction and adaptation to different situations.
Integration
The central nervous system (CNS), which includes the brain and spinal cord, processes and integrates incoming sensory information. This function allows for the interpretation of the data collected from the environment and the body’s internal state.
After processing, the CNS coordinates appropriate responses, ensuring that the body reacts effectively to various stimuli. This integration is crucial for maintaining homeostasis and enabling complex behaviors, as it allows for a coordinated and timely reaction to changes and challenges in the surroundings.
Motor Output
The CNS is responsible for generating motor responses, which lead to actions such as muscular contractions or glandular secretions. This capability enables the organism to actively respond to stimuli.
For example, when the brain processes information and decides on a course of action, it sends signals through the nervous system to the muscles or glands, triggering them to contract, move, or release substances.
These responses can be voluntary, like moving an arm, or involuntary, like the secretion of digestive enzymes, allowing the organism to interact with and adapt to its environment effectively.
Homeostasis
The CNS is essential in maintaining homeostasis, the stable state of internal conditions within the body. It regulates key factors like temperature, blood pressure, and blood glucose levels.
By constantly monitoring and adjusting these and other vital parameters, the nervous system ensures that the body’s internal environment remains stable despite external changes. This regulation is vital for the body’s optimal functioning and survival, as it keeps critical conditions within the narrow limits necessary for life
Learning and Memory
The nervous system plays a pivotal role in learning and memory, enabling organisms to adapt and modify their behaviors based on past experiences. Through these processes, the brain can encode, store, and retrieve information, allowing individuals to learn from their environment and adjust their actions accordingly. This capacity for learning and memory is fundamental to an organism’s ability to navigate complex environments, solve problems, and make decisions, reflecting the intricate and dynamic nature of neural functions in supporting cognitive development and behavioral adaptation.
Emotional Responses
The CNS significantly impacts emotional responses and mood by facilitating complex interactions between the brain and various neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that transmit signals across nerve cells, influencing feelings of happiness, sadness, anxiety, and excitement.
The brain processes these signals, leading to the experience of different emotions. This network of interactions allows the nervous system to regulate emotional responses to external events and internal thoughts, playing a crucial role in psychological well-being and the overall mental health of an individual.
Coordination and Control
The nervous system is pivotal in coordinating and controlling the activities of various organs and systems within the body, ensuring they operate in harmony. It acts like a command center, sending and receiving information through nerve signals to regulate bodily functions.
This coordination is crucial for maintaining overall health and enabling complex processes such as movement, digestion, and the body’s response to stress. By synchronizing the actions of different body parts, the nervous system helps maintain a stable and efficient internal environment, allowing the organism to function effectively in response to various internal and external demands.
Related Links
Anatomy
Epithelial Tissue
Immune System
Synapse