Nucleotide
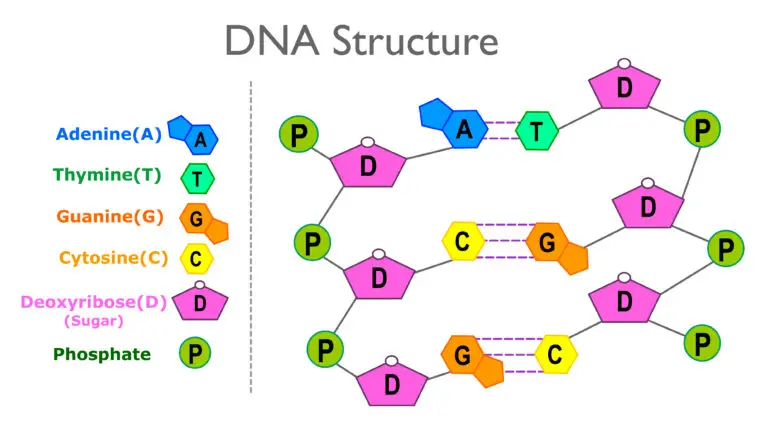
Table of Contents
What is a Nucleotide?
A nucleotide is a fundamental building block of nucleic acids, which are the informational molecules essential for the storage and transmission of genetic information in living organisms. Nucleotides are the monomers or basic units that make up nucleic acids, including DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid).
Overview of Nucleotides
Phosphate Group (PO₄)
The phosphate group is a chemical group consisting of phosphorus and oxygen atoms. In a nucleotide, the phosphate group is attached to the sugar molecule. It provides a negative charge to the nucleotide.
Sugar Molecule
In DNA, the sugar molecule is deoxyribose, and in RNA, it is ribose. The sugar is a five-carbon (pentose) molecule that forms the backbone of the nucleotide. The carbon atoms in the sugar are numbered 1′ through 5′.
Nitrogenous Base
The nitrogenous base is a nitrogen-containing molecule that is attached to the sugar molecule. There are four types of nitrogenous bases in DNA: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). In RNA, thymine is replaced by uracil (U). The sequence of these bases encodes genetic information.
Types of Nucleotides
Deoxyribonucleotide: Found in DNA, it has deoxyribose as the sugar molecule.
Ribonucleotide: Found in RNA, it has ribose as the sugar molecule.
Roles of Nucleotides
Genetic Information: Nucleotides serve as the units of genetic information in DNA and RNA. The sequence of nucleotides in these molecules encodes the instructions for the synthesis of proteins and other cellular activities.
Energy Transfer: Nucleotides, especially those with high-energy bonds (e.g., ATP – adenosine triphosphate), are involved in energy transfer within cells. ATP, in particular, is a primary energy carrier in cellular processes.
Coenzymes: Nucleotides are components of coenzymes, which are essential for various enzymatic reactions in cellular metabolism.
Cellular Signaling: Nucleotides, such as cyclic AMP (cAMP), play a role in cellular signaling pathways, transmitting signals within cells.
Related Links
Base Pair
Denaturation
Deoxyribose
Thylakoid