Nucleus
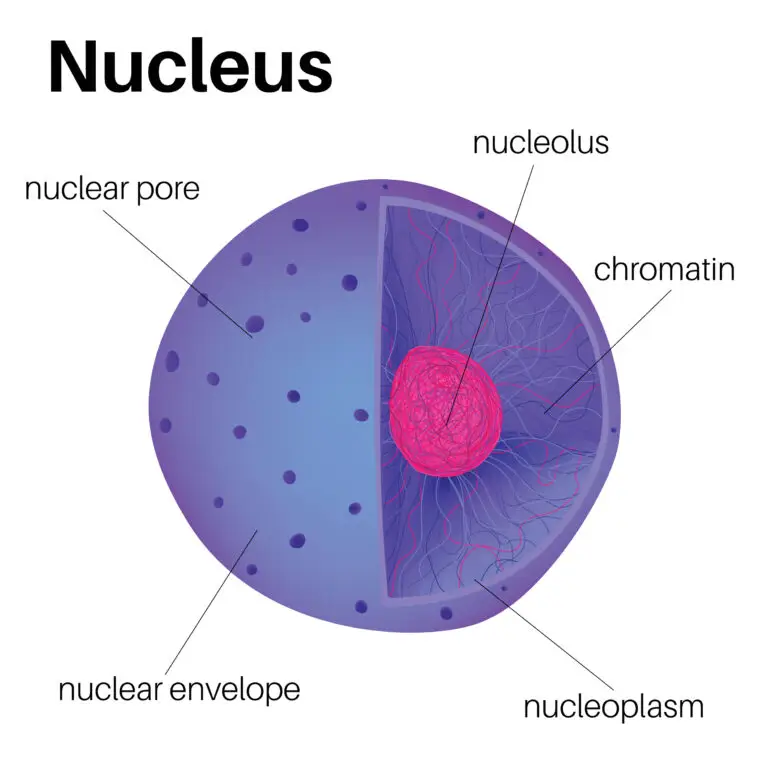
Table of Contents
What is a Nucleus?
The nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. It serves as the central hub for the control and regulation of cellular activities, particularly those related to genetic information. The nucleus contains the cell’s genetic material in the form of chromosomes, which carry the instructions for the synthesis of proteins and the overall functioning of the cell.
Features and Functions of the Nucleus
Nuclear Envelope
The nucleus is surrounded by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope. The nuclear envelope has pores that control the passage of molecules between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
Chromosomes
Within the nucleus, genetic material is organized into structures called chromosomes. Chromosomes consist of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and associated proteins. The DNA carries the instructions for building and maintaining the organism.
Nucleolus
The nucleolus is a distinct region within the nucleus where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is synthesized and ribosomal subunits are assembled. Ribosomes, the cellular structures responsible for protein synthesis, are partially assembled in the nucleolus.
Genetic Information
The nucleus contains the hereditary information necessary for the growth, development, and functioning of the cell and the entire organism. This genetic information is stored in the form of genes on the DNA molecules.
Transcription
Transcription, the process of synthesizing RNA from DNA, occurs in the nucleus. Messenger RNA (mRNA) is transcribed from specific genes and carries the genetic code to the cytoplasm, where protein synthesis takes place.
DNA Replication
DNA replication, the process of copying the genetic material to ensure the accurate transmission of genetic information during cell division, occurs in the nucleus.
Cellular Regulation
The nucleus plays a central role in regulating cellular activities by controlling gene expression. Gene expression involves the activation or suppression of specific genes, influencing the production of proteins and other cellular components.
Cell Division
During cell division, the nucleus undergoes a process called mitosis, where the replicated chromosomes are distributed to daughter cells. In eukaryotic organisms, mitosis ensures the inheritance of genetic material by offspring cells.
Related Links
Cloning
Electrons
Gene Expression
Proton