Organelle
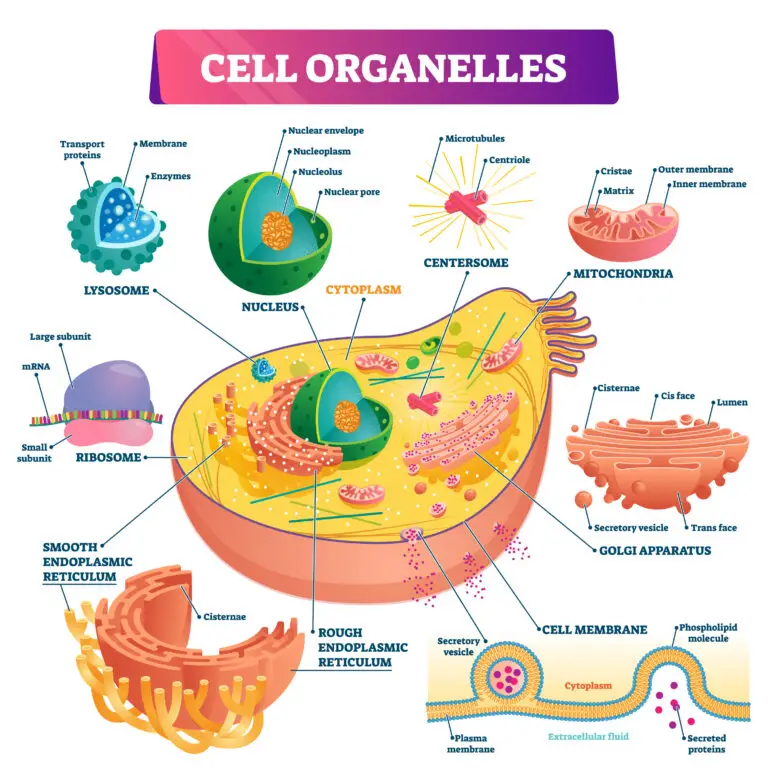
Table of Contents
What is an Organelle?
An organelle is a specialized subunit or structure within a cell that performs specific functions, contributing to the overall functioning of the cell. These membrane-bound structures are often compared to the organs in a multicellular organism, as they carry out distinct tasks that are essential for the cell’s survival, growth, and reproduction.
Characteristics of Organelles
Membrane-Bound Structures
Many organelles are enclosed by a membrane, which separates their internal environment from the surrounding cytoplasm. This membrane serves as a barrier and helps regulate the flow of substances in and out of the organelle.
Specialized Functions
Each organelle has a specific role or function within the cell. These functions can range from energy production and cellular respiration to protein synthesis and waste disposal.
Coordination and Cooperation
Organelles work in coordination with each other to carry out the various processes necessary for the cell’s survival. The cooperation of organelles contributes to the overall functioning of the cell.
Structural Organization
Organelles are distributed throughout the cytoplasm and exhibit a degree of structural organization within the cell. Their arrangement is crucial for maintaining cellular integrity and facilitating cellular processes.
Sister Chromatids
Before cell division, each chromosome replicates, resulting in two identical copies called sister chromatids.
Sister chromatids are held together at the centromere and are eventually separated during cell division, ensuring that each daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes.
Examples of Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells
Nucleus: The nucleus is the central organelle that houses the cell’s genetic material (DNA) and controls cellular activities, including gene expression and DNA replication.
Mitochondria: Mitochondria are the organelles responsible for energy production through cellular respiration. They generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy currency of the cell.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of membranes involved in protein synthesis, folding, and transport. It can be rough (with ribosomes) or smooth (lacking ribosomes), serving different functions.
Golgi Apparatus: The Golgi apparatus is involved in processing, modifying, and packaging proteins for secretion or delivery to other cellular locations.
Lysosomes: Lysosomes are membrane-bound vesicles containing enzymes that break down cellular waste, foreign materials, and worn-out organelles through a process known as autophagy.
Peroxisomes: Peroxisomes are involved in various metabolic processes, including the breakdown of fatty acids and the detoxification of harmful substances.
Ribosomes: Ribosomes are involved in protein synthesis. They can be found free in the cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum.
Vacuoles: Vacuoles are membrane-bound sacs that store water, nutrients, and waste products. In plant cells, the central vacuole plays a role in maintaining turgor pressure.
Cytoskeleton: While not a single organelle, the cytoskeleton is a network of protein filaments (microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments) that provides structural support, maintains cell shape, and facilitates intracellular transport.
Chloroplasts: Found in plant cells and some protists, chloroplasts are involved in photosynthesis, where they capture sunlight and convert it into chemical energy in the form of glucose.
Related Links
Biogenesis
Chloroplast
Symbiosis
Turgor Pressure