Real Number
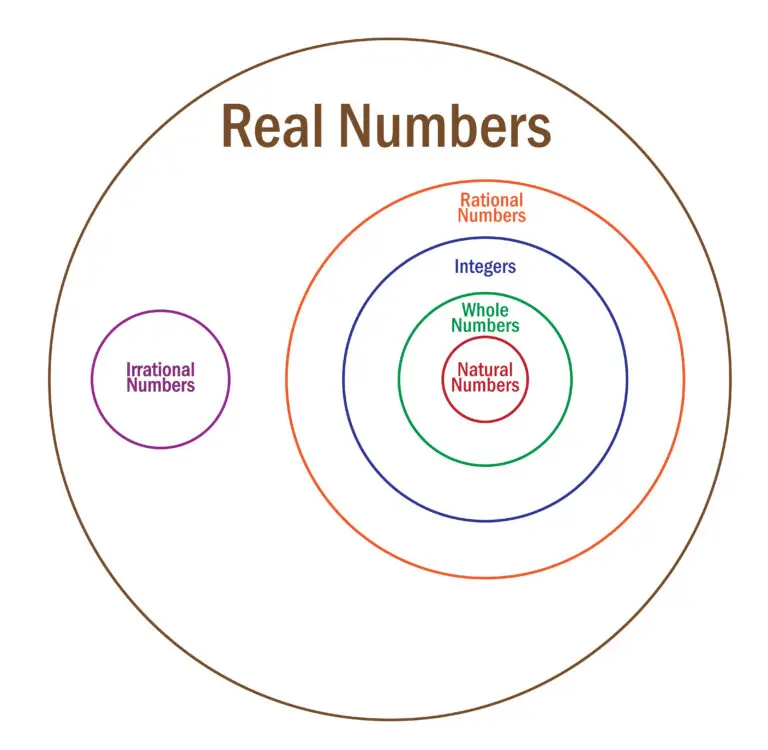
Table of Contents
What is a Real Number?
A real number is a quantity that can be represented on the number line. Real numbers include rational numbers, which can be expressed as fractions, and irrational numbers, which cannot be expressed as fractions.
Real numbers encompass a broad range of mathematical quantities, and every point on the number line corresponds to a real number.
Representation on the Number Line
Every real number can be located on the number line, which extends infinitely in both directions.
Includes Rational and Irrational Numbers
Real numbers encompass both rational numbers (fractions) and irrational numbers (non-repeating, non-terminating decimals).
Expressible as Decimals or Fractions
Real numbers can be expressed in decimal form, fractional form, or as square roots of non-negative numbers.
Classification of Real Numbers
Rational Numbers: Numbers that can be expressed as the quotient or fraction of two integers, where the denominator is not zero. Examples include \frac{3}{4},\text{-}\frac{5}{2}, and 0.
Irrational Numbers: Numbers that cannot be expressed as fractions. Examples include \sqrt{2}, \pi, and e.
Integers: Whole numbers, including positive, negative, and zero. Examples include \text{-}3, 0, 5.
Whole Numbers: Non-negative integers. Examples include 0, 1, 2.
Natural Numbers: Positive integers excluding zero. Examples include 1, 2, 3.
Related Links
Complex Number
Imaginary Unit
Irrational Number
Rational Number