Redox Reaction
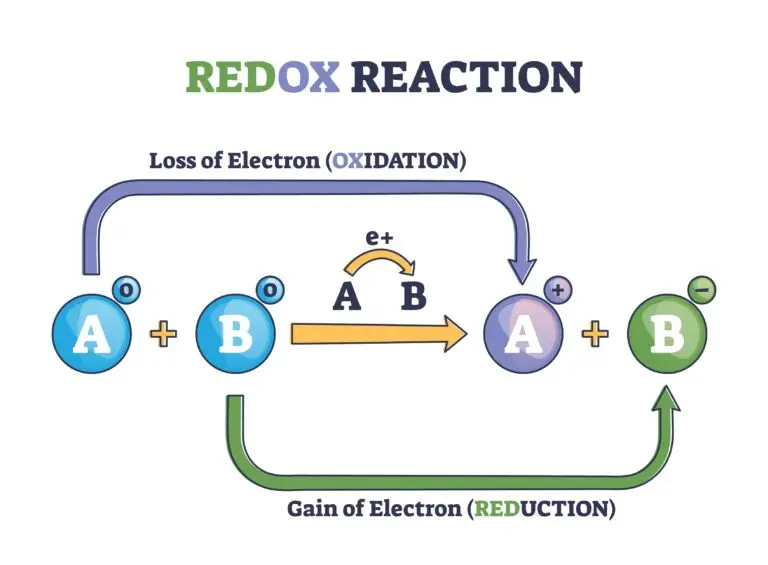
Table of Contents
What is a Redox Reaction?
A redox reaction, short for reduction-oxidation reaction, is a chemical process in which one substance loses electrons (undergoes oxidation) while another substance gains electrons (undergoes reduction). These reactions involve the transfer of electrons from one chemical species to another, and they are fundamental to various biological, chemical, and electrochemical processes.
Key Concepts of Redox Reactions
Oxidation and Reduction
- Oxidation: The loss of electrons by a substance. The substance undergoing oxidation is referred to as the reducing agent.
- Reduction: The gain of electrons by a substance. The substance undergoing reduction is referred to as the oxidizing agent.
Electron Transfer
In a redox reaction, electrons are transferred from the reducing agent to the oxidizing agent. The reducing agent is oxidized because it loses electrons, and the oxidizing agent is reduced because it gains electrons.
Half-Reactions
Redox reactions are often described as two half-reactions: the oxidation half-reaction and the reduction half-reaction. The overall redox reaction is the sum of these two half-reactions.
Oxidation State
The oxidation state (or oxidation number) of an element reflects the number of electrons it has gained or lost. An increase in oxidation state indicates oxidation, while a decrease indicates reduction.
Balancing Redox Reactions
Balancing redox reactions involves ensuring that the number of electrons lost in the oxidation half-reaction is equal to the number gained in the reduction half-reaction. This balance can be achieved by adjusting coefficients and charges.
Electrochemical Cells
Many redox reactions are involved in electrochemical cells, such as batteries. In these cells, chemical energy is converted into electrical energy through redox reactions.
Related Links
Chemical Reaction
Reactant
Catalyst (Chemistry)
Exothermic Reaction