Sample
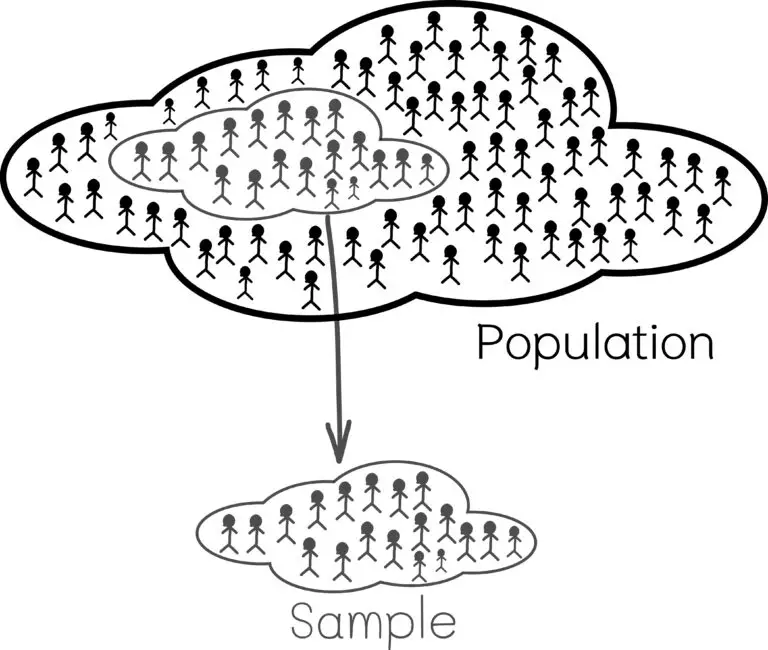
Table of Contents
Statistics Sample
A sample refers to a subset of individuals, items, or observations selected from a larger population for the purpose of conducting a study or analysis. Samples are used because it is often impractical or impossible to collect data from an entire population due to factors such as time, cost, and feasibility.
Random Sampling
Random sampling involves selecting individuals from a population in such a way that every member of the population has an equal chance of being included in the sample. This helps ensure that the sample is representative of the population and reduces bias.
Types of Samples
- Simple Random Sample: Each member of the population has an equal probability of being selected.
- Stratified Sample: The population is divided into subgroups (strata), and samples are then randomly selected from each stratum.
- Cluster Sample: The population is divided into clusters, and clusters are randomly selected. All members within the selected clusters are included in the sample.
- Systematic Sample: Every nth member of the population is selected to be part of the sample, starting from a randomly chosen individual.
Sample Size
The sample size refers to the number of individuals or observations included in the sample. A larger sample size generally provides more precise estimates and increases the reliability of statistical analyses.
Representativeness
A representative sample is one that accurately reflects the characteristics of the population. Achieving representativeness is essential for generalizing findings from the sample to the entire population.
Sampling Techniques
Various sampling techniques are used depending on the research design, study objectives, and population characteristics. Choosing an appropriate sampling method is crucial for obtaining valid and reliable results.
Inferential Statistics
Sample data are used to estimate population parameters and make inferences about the population. Inferential statistics involve using sample statistics to draw conclusions about population parameters and test hypotheses.
Related Links
Association
Chance Error
Control Group
Variance