Snowball Sampling
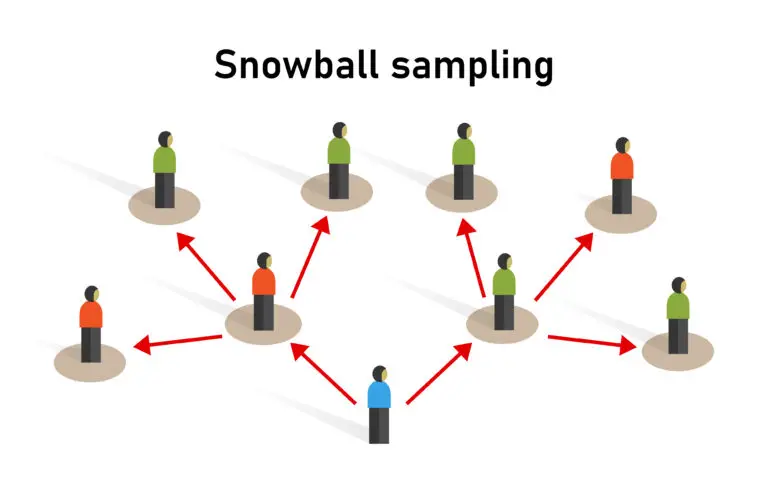
Table of Contents
What is Snowball Sampling?
Snowball sampling is a non-probability sampling technique used in qualitative research and social sciences, particularly when studying populations that are difficult to access or identify through traditional sampling methods.
In snowball sampling, initial participants, known as “seeds,” are selected, and then they refer or nominate additional participants from their social networks who meet the study criteria. This method allows researchers to reach hidden or marginalized populations and study interconnected social networks.
Snowball Sampling Process
- The process starts with identifying a few initial participants, often referred to as “seeds.” These individuals are typically knowledgeable about the study topic and have connections within the target population.
- The seeds are interviewed or surveyed, and after participating in the study, they are asked to refer or nominate other individuals from their social circles who fit the study criteria and are willing to participate.
- The process continues iteratively, with new participants referring additional participants, hence the name “snowball,” as the sample size grows like a snowball rolling downhill.
Characteristics
- Snowball sampling is particularly useful for studying hidden or hard-to-reach populations, such as minority groups, marginalized communities, illegal activities, or sensitive topics where participants may be reluctant to participate.
- It relies on social networks and referrals, allowing researchers to access interconnected social groups and study relationships and networks within the population.
Advantages
- Accessibility: Snowball sampling allows researchers to access populations that may be difficult to reach through traditional sampling methods, such as random sampling or stratified sampling.
- Cost-Effective: Compared to other sampling techniques that require extensive resources for participant recruitment, snowball sampling can be cost-effective as it relies on participant referrals.
- Network Analysis: It facilitates the study of social networks, relationships, and interconnectedness within the population, providing insights into social structures and dynamics.
Limitations
- Bias: Snowball sampling can introduce bias into the sample, as participants are selected based on referrals and connections within social networks. This can result in overrepresentation of certain characteristics or perspectives.
- Lack of Generalizability: The findings from snowball sampling may not be generalizable to the broader population, as the sample is not randomly selected and may not be representative.
- Difficulty in Estimating Sampling Error: Since snowball sampling does not follow a probabilistic sampling method, estimating sampling error and statistical precision can be challenging.
Ethical Considerations
Researchers must consider ethical issues such as informed consent, confidentiality, privacy, and the potential for coercion or undue influence, especially when studying sensitive topics or vulnerable populations.
Applications of Snowba
Snowball sampling is commonly used in qualitative research, ethnographic studies, social network analysis, studies of hidden populations (e.g., drug users, sex workers), and exploratory research on emerging or understudied topics.
Related Links
Bias
Central Limit Theorem
Simple Random Sample
Statistic