Tissue
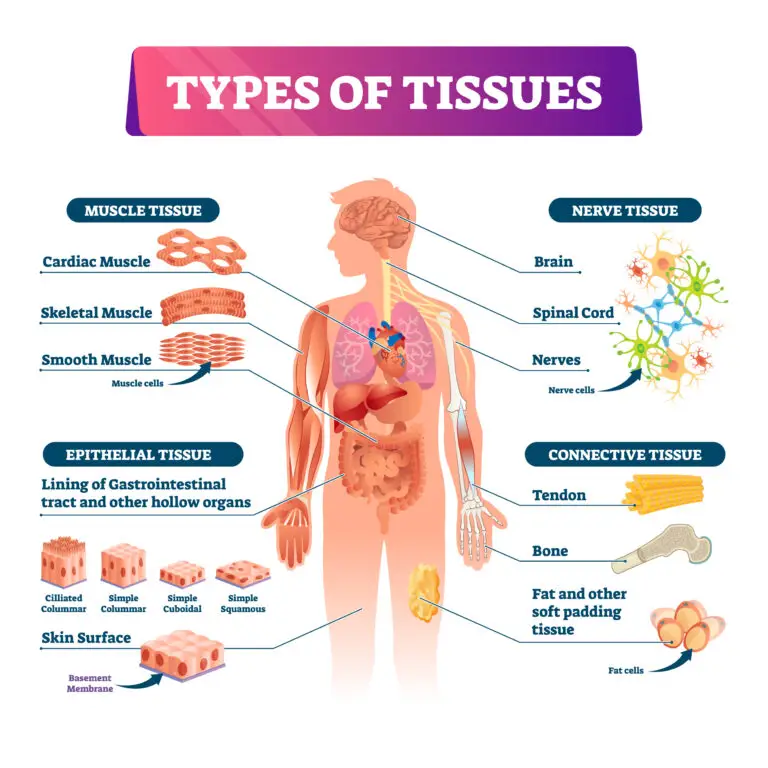
Table of Contents
Tissue Definition
Tissue is a group of cells that are similar in structure and function, and they work together to perform a specific set of tasks within an organism. They are organized into larger functional units called organs, and organs, in turn, contribute to the structure and function of organ systems.
Biological Tissue
Composition
Tissues are composed of cells that are structurally and functionally similar. The cells within a tissue type often have specific shapes and characteristics contributing to their specialized function.
Histological Classification
Histologists classify tissues based on their microscopic structure and the arrangement of cells. Each type has characteristic features that can be observed under a microscope.
Function
Tissues work together to perform specific functions necessary for the survival and proper functioning of the organism. For example, the epithelial tissue in the skin provides a protective barrier, connective tissue supports and binds organs, and muscle tissue enables movement.
Organ and System Organization
Tissue combine to form organs, and organs, in turn, contribute to the structure and function of organ systems. The coordinated activity of tissues at different levels of organization ensures the proper functioning of the organism as a whole.
Types of Animal Tissues
-
Epithelial:
- Location: Covers body surfaces, lines cavities, and forms glands.
- Function: Provides protection, absorption, secretion, and sensation.
-
Connective:
- Location: Throughout the body, supporting and connecting tissues and organs.
- Function: Provides structural support, binds tissues together, stores energy, and transports substances.
-
Muscle:
- Location: Attached to bones (skeletal muscle), in the walls of internal organs (smooth muscle), and in the heart (cardiac muscle).
- Function: Enables movement, maintains posture, and generates force.
-
Nervous:
- Location: Brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves.
- Function: Transmits electrical impulses, processes information, and coordinates responses.
Plant Tissues
In plants, tissues are organized into three main types:
- Dermal: Covers and protects the plant.
- Ground: Provides support and storage.
- Vascular: Facilitates the transport of water, nutrients, and sugars.
Related Links
Anatomy
Biotechnology
Epithelial Tissue
Immune System