Transcription
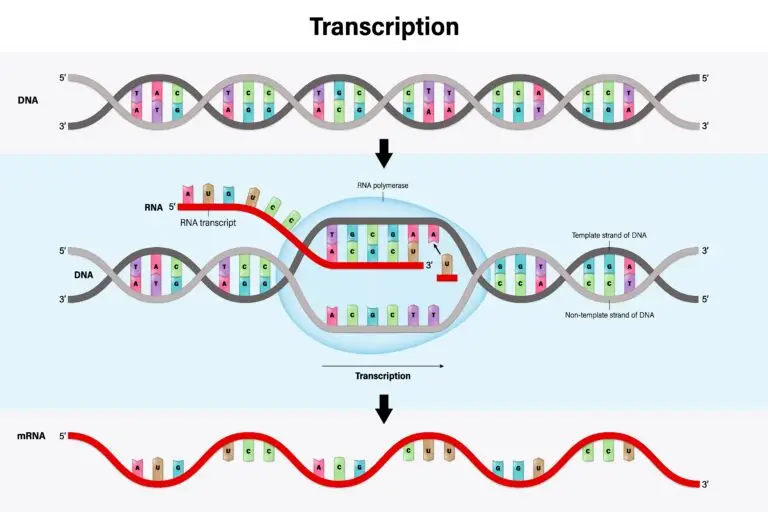
Table of Contents
What is Transcription?
Transcription is a fundamental process in molecular biology where genetic information encoded in DNA is used to synthesize a complementary RNA molecule. This RNA molecule, or messenger RNA (mRNA), carries the genetic instructions from the DNA to the ribosomes, where protein synthesis (translation) occurs.
Steps of Transcription
Initiation
Transcription begins with binding an enzyme called RNA polymerase to a specific region of DNA known as the promoter. The promoter signals the starting point for transcription.
Elongation
During elongation, RNA polymerase moves along the DNA template strand, synthesizing a complementary RNA strand. It adds complementary RNA nucleotides (adenine, cytosine, guanine, and uracil) to the growing RNA chain.
Termination
Transcription concludes with termination, where RNA polymerase reaches a termination sequence in the DNA. This sequence signals the end of the gene, and the RNA polymerase detaches from the DNA template. The newly synthesized RNA molecule is released.
Components Involved in Transcription
RNA Polymerase
RNA polymerase is the enzyme responsible for catalyzing the synthesis of RNA from a DNA template during transcription. A single type of RNA polymerase is involved in prokaryotes, while in eukaryotes, there are multiple RNA polymerases.
DNA Template
The DNA sequence that serves as a template for RNA synthesis is known as the DNA template strand. The complementary RNA strand is synthesized based on this template.
Promoter
The promoter is a specific DNA region that signals the transcription starting point. RNA polymerase binds to the promoter to initiate the process.
Terminator
The terminator is a sequence in DNA that signals the end of the gene and transcription. It prompts the detachment of RNA polymerase from the DNA template.
Nucleotides
RNA nucleotides (adenine, cytosine, guanine, and uracil) are building blocks during transcription. They are added to the growing RNA chain in a sequence complementary to the DNA template.
Related Links
Denaturation
Gene Expression
Genetic Code
Translation