Urea
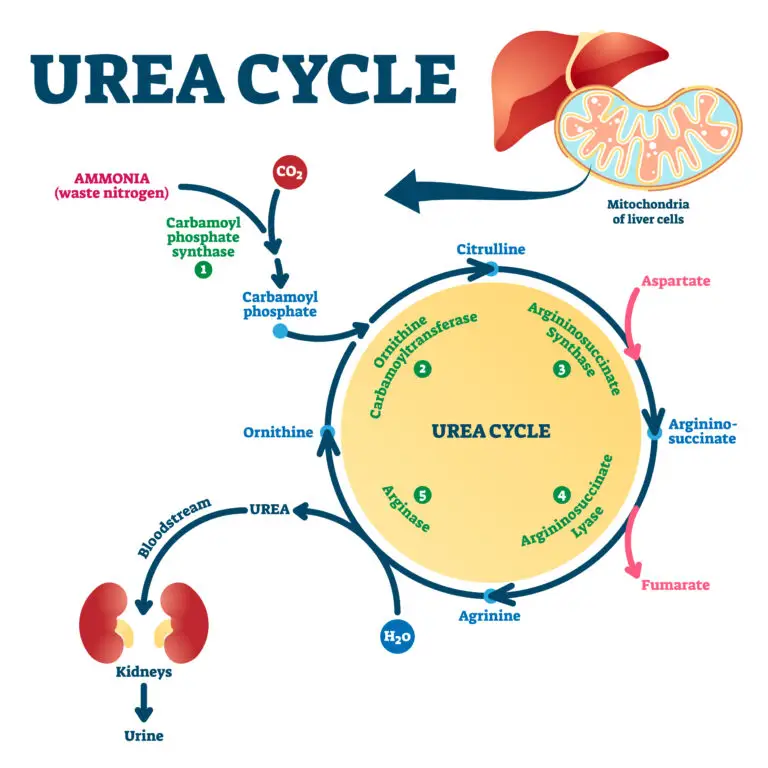
Table of Contents
What is Urea?
Urea is a chemical compound with the molecular formula CO(NH₂)₂. It is a compound that contains carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen and is produced in the liver of animals, including humans, as a byproduct of metabolism. Urea is a nitrogen-containing waste product that is excreted from the body through urine.
Key Points about Urea
Chemical Formula
The chemical formula of urea is CO(NH₂)₂, indicating that it consists of one carbon (C) atom, one oxygen (O) atom, and four hydrogen (H) atoms.
Metabolic Byproduct
Urea is produced in the liver during the breakdown of proteins and amino acids. It is a major component of urine and is excreted from the body through the kidneys.
Nitrogen Elimination
One of the primary functions of urea is to eliminate excess nitrogen from the body. Nitrogen is a byproduct of protein metabolism, and urea provides a way for the body to remove and excrete excess nitrogen safely.
Solubility
Urea is highly soluble in water, and it easily dissolves in urine. Its solubility makes it an effective vehicle for transporting nitrogenous waste out of the body.
Fertilizer
Urea is also used as a nitrogen-rich component in fertilizers. It provides a source of nitrogen that plants can absorb and utilize for growth. In agriculture, urea is often applied to soil as a nitrogen fertilizer.
Medical Uses
Urea is sometimes used in certain medical and cosmetic products. In dermatology, it may be included in creams and lotions for its moisturizing properties.
Laboratory Applications
Urea is used in various laboratory procedures and experiments. It is a common reagent in biochemistry and molecular biology for applications such as protein denaturation and as a component of buffer solutions.
Amide Bond
Urea contains an amide bond (CO-NH₂), which is a functional group formed by the combination of a carbonyl group (C=O) and an amino group (NH₂).
Related Links
Excretion
Metabolism
Nitrogen Cycle
Placenta