Variable
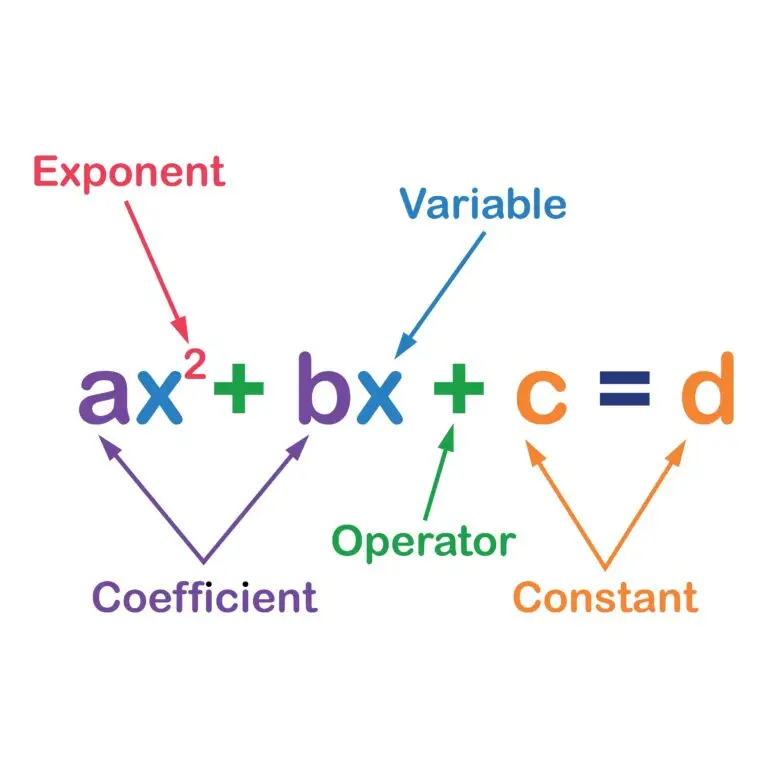
Table of Contents
What is a Variable?
A variable is a symbol or letter that represents a number or an unknown quantity. Variables are used to formulate algebraic expressions and equations, allowing for the representation of mathematical relationships and patterns.
Typically denoted by letters like x, y, or z, variables can take on different values, and their manipulation allows for the exploration and solution of mathematical problems.
Characteristics
Symbolic Representation
A variable is represented by a letter or symbol.
Unknown or Generic Quantity
The value of a variable is not fixed; it can represent any number or quantity.
Used in Expressions and Equations
Variables are employed to create algebraic expressions and equations to model mathematical situations.
Examples of Variables
Simple Variable:
- x: Here, x is a variable representing an unknown quantity. It could take on any real number value.
Two Variables:
- y, z: Variables can be denoted by different letters. For example, y and z can represent other unknown quantities.
Variables in Expressions:
- 2x+3: In the expression 2x+3, x is a variable, and the expression represents a quantity that depends on the value assigned to x.
Variables in Equations:
- 4y=12: In the equation 4y=12, y is a variable, and solving the equation determines the value of x.
Using Subscripts:
- A_n: Subscripts can be used to indicate a specific variable in a sequence; for instance, A_n represents a variable in a sequence with n as an index.
Related Links
Constant
Cross-Multiplication
Linear Equation
Inequality