Vesicle
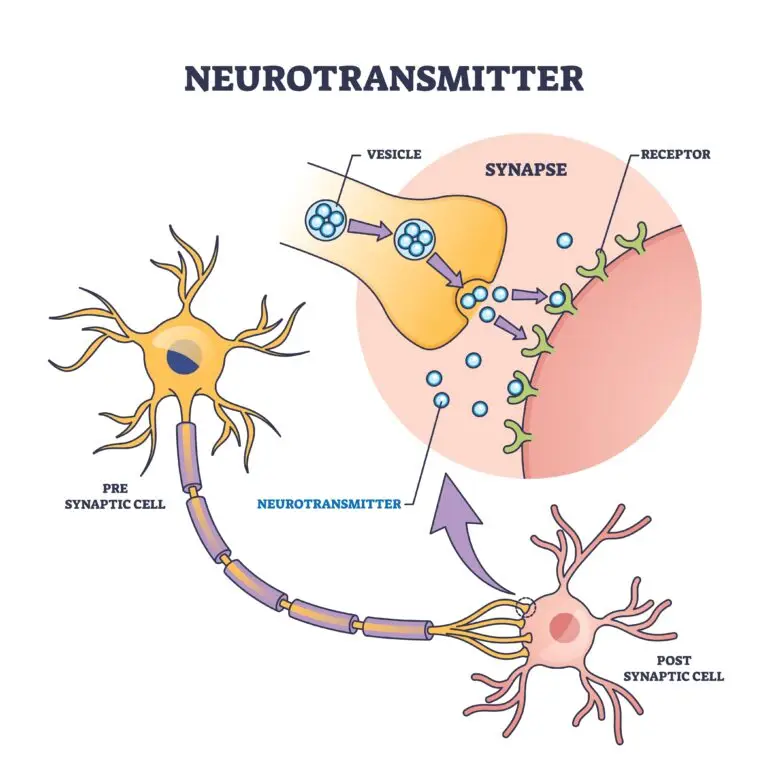
Table of Contents
What is a Vesicle?
A vesicle is a small, membrane-bound sac that plays various roles in cellular transport, storage, and communication. Vesicles are essential cell components, helping transport and compartmentalize molecules within the cell and facilitating interactions between different cellular organelles.
Key Features of Vesicles
Membrane Structure
A lipid bilayer, similar to the cell membrane, encloses vesicles. This membrane structure allows vesicles to separate their contents from the surrounding cellular environment.
Transport Vehicles
Vesicles are often involved in intracellular transport, moving molecules within the cell. This can include transporting proteins, lipids, and other cellular materials between organelles.
Formation and Budding
Vesicles are formed through budding or pinching off from a membrane. The membrane surrounding the vesicle is derived from the membrane of an organelle or the cell membrane itself.
Cargo Containment
Vesicles can carry a variety of cargo, including proteins, enzymes, hormones, and cellular waste. They help to compartmentalize these substances, allowing for organized cellular processes.
Types of Vesicles and Their Functions
Endocytic Vesicles
Endocytic vesicles are involved in endocytosis, where cells take in substances from the external environment. This can include the formation of phagosomes (engulfing solid particles) and pinocytic vesicles (engulfing liquid or dissolved substances).
Exocytic Vesicles
Exocytic vesicles are involved in exocytosis, the process by which cells release substances to the external environment. This can include the secretion of hormones, enzymes, or other cellular products.
Transport Vesicles
Transport vesicles move molecules between different cellular compartments. For example, they may transport proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to the Golgi apparatus.
Synaptic Vesicles
Synaptic vesicles are found in nerve cells and store neurotransmitters. When an action potential reaches the synapse, synaptic vesicles release neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft, allowing communication between nerve cells.
Lysosomes
Lysosomes are membrane-bound vesicles with enzymes capable of breaking down cellular waste, damaged organelles, and foreign materials. They play a role in cellular digestion and recycling.
Vacuoles
In plant cells, vacuoles are large vesicles that store substances such as water, ions, and nutrients. Vacuoles also contribute to maintaining turgor pressure in plant cells.
Endosomal Vesicles
Endosomal vesicles are involved in the sorting and trafficking molecules within the endocytic pathway. They can mature into early endosomes and late endosomes and eventually fuse with lysosomes for degradation.
Related Links
Digestion
Lysosome
Organelle
Synapse