Asexual Reproduction
What is Asexual Reproduction?
Asexual reproduction is a mode of reproduction where an organism creates offspring without the involvement of gametes (sperm and egg). In asexual reproduction, offspring are genetically identical to the parent, allowing rapid population growth in favorable conditions.
Making Babies Without a Partner
Asexual reproduction is when an animal or plant creates offspring (babies) without needing a mate. The new organism is an exact copy, or clone, of the parent. It’s like making a duplicate of yourself!
How Asexual Reproduction Works
In asexual reproduction, one parent produces offspring on its own. There’s no need to find a mate or combine DNA. The new organism gets all its traits from the one parent, so it looks just like it.
Examples
- Budding: A tiny version of the parent grows out of its body, like a hydra.
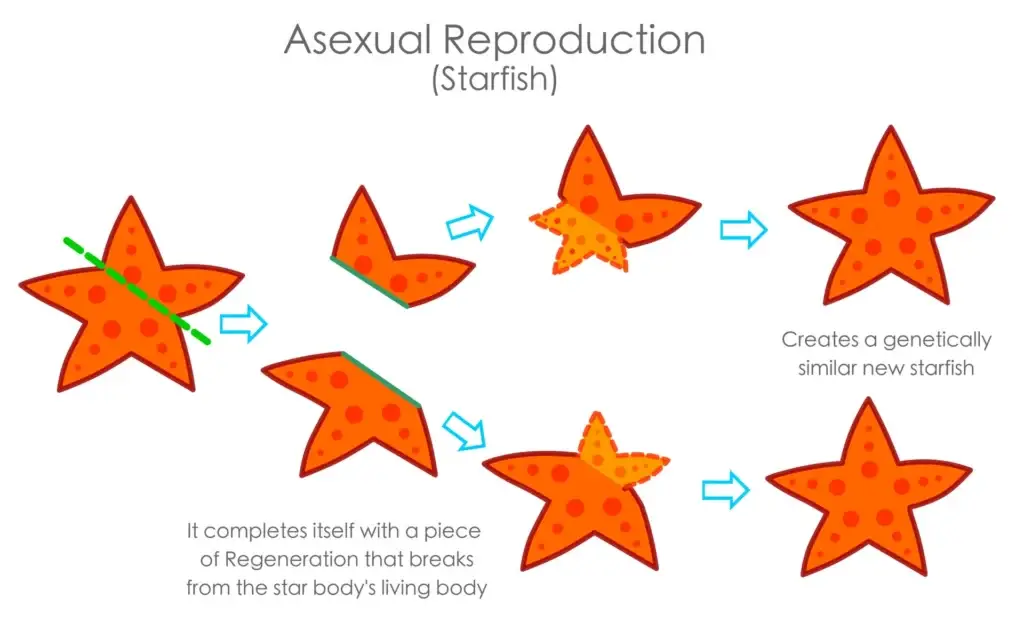
- Fragmentation: Some animals, like starfish, regrow a whole new body from a piece that breaks off.
- Binary Fission: Simple organisms like bacteria split in half to make two identical organisms.
- Parthenogenesis: Some insects and lizards lay eggs that hatch without fertilization.
Why Animals Use Asexual Reproduction
- Quick and Easy: Asexual reproduction is faster since no partner is needed.
- Stable Environments: It works well when conditions don’t change much, so the offspring can survive like the parent.
- High Numbers: Many offspring can be produced quickly, which helps species grow fast.
Challenges of Asexual Reproduction
- No Genetic Variety: All offspring are identical, which can be a problem if the environment changes or a disease spreads.
- Limited Adaptability: Without new traits, it’s harder for a species to survive in changing conditions.
Where Asexual Reproduction Happens
- In Simple Animals: Like hydras, sponges, and starfish.
- In Plants: Many plants grow new copies of themselves through runners or cuttings.
- In Microorganisms: Bacteria and amoebas use asexual reproduction to multiply quickly.
How It’s Different From Sexual Reproduction
- Asexual: One parent, identical offspring.
- Sexual: Two parents, offspring with a mix of traits.