Evolution
What is Evolution?
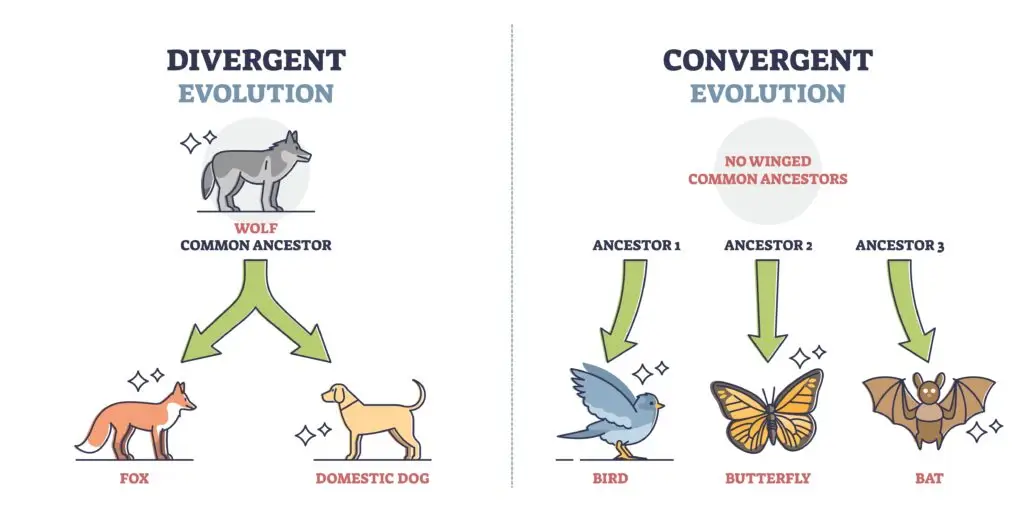
Evolution is the gradual process by which species change over time through genetic variation and natural selection. Evolution leads to the development of new traits and, eventually, new species as organisms adapt to their environments.
How Animals Change Over Time
Evolution is the process by which animals and other living things slowly change over many generations to adapt to their environment. These changes help species survive, find food, and reproduce.
How Evolution Works
Evolution happens through a process called natural selection:
- Variation: Animals in a species are a little different from each other. For example, some birds may have longer beaks.
- Survival: Animals with traits that help them survive are more likely to live and have babies.
- Passing Down Traits: These helpful traits, like a longer beak, are passed to the next generation. Over time, the species changes.
Examples of Evolution
- Peppered Moths: During the Industrial Revolution, darker moths survived better because they blended into soot-covered trees. Over time, most moths became dark.
- Finches in the Galápagos: Different islands have finches with different beak shapes, each adapted to eating specific foods like seeds or insects.
- Whales: Evolved from land animals millions of years ago to live in the ocean.
Why Evolution Is Important
Evolution explains:
- Adaptations: Why animals have special traits, like polar bears’ thick fur for the cold.
- Biodiversity: How the variety of life on Earth has grown over millions of years.
- Extinctions: Why some species disappear when they can’t adapt quickly enough.
Natural Selection in Animal Populations
Natural selection is a key idea in zoology that explains how animal populations change over time. In natural selection, animals with traits that help them survive and reproduce are more likely to pass these traits to their offspring.
Over many generations, these helpful traits become more common in the population, making animals better suited to their environment. Zoologists study natural selection to see how things like food, weather, and predators affect animal traits. This process is one reason why animals today are so diverse, with different shapes, sizes, and behaviors suited to their environments.