Homeostasis
Definition of Homeostasis
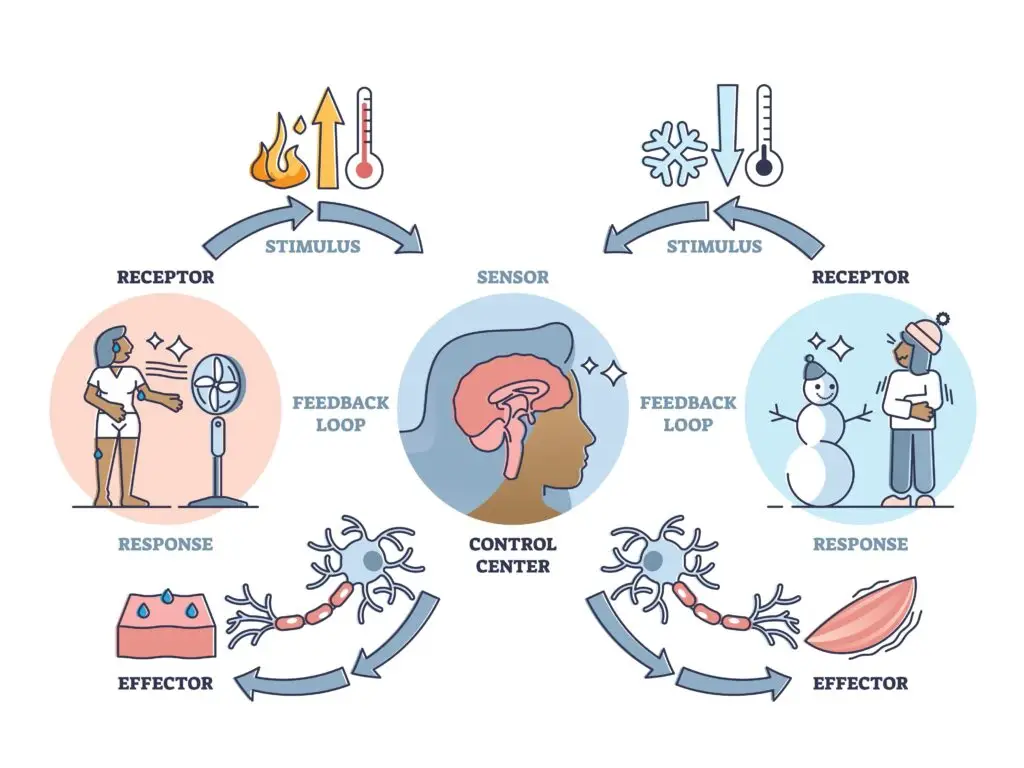
Homeostasis is the process by which an organism maintains stable internal conditions, such as temperature and pH, despite changes in its external environment. Homeostasis is essential for optimal functioning and survival.
Keeping the Body Balanced
Homeostasis is how your body keeps everything balanced and working correctly. It makes sure things like your temperature, water levels, and energy stay just right, no matter what’s happening around you.
How Homeostasis Works
Your body has special systems to keep everything in balance:
- Temperature Control: If you’re too hot, you sweat to cool down. If you’re too cold, you shiver to warm up.
- Water Balance: When you’re thirsty, your body tells you to drink. If you drink too much, you get rid of the extra water by peeing.
- Energy Levels: When your energy is low, your body tells you to eat. After eating, your body stores the energy for later.
Examples of Homeostasis
- Blood Sugar: If your sugar levels are too high, your body releases insulin to bring it down.
- Breathing: When you run, your body breathes faster to get more oxygen to your muscles.
- Heart Rate: Your heart beats faster when exercising and slows down when you rest.
Importance to Health
Homeostasis keeps your body working properly:
- Staying Healthy: It prevents your body from overheating, dehydrating, or running out of energy.
- Quick Reactions: It helps your body adjust to changes, like running from danger or cooling off on a hot day.
- Preventing Illness: If homeostasis doesn’t work, you might get sick.
Supports Homeostasis
Metabolism and homeostasis work together to keep our bodies balanced and healthy. Metabolism is all the chemical reactions in the body that turn food into energy and build or repair cells. This energy powers all the body’s activities, like moving, breathing, and even thinking.
Homeostasis is the process of keeping internal conditions, like body temperature, blood sugar, and pH levels, stable even when things around us change. Metabolism supports homeostasis by providing the energy needed to maintain these stable conditions. For example:
- When it’s cold, metabolism speeds up to produce extra heat, helping to keep our body temperature steady.
- After eating, metabolism works to break down food and adjust blood sugar levels, keeping them from getting too high or too low.
By constantly adjusting and providing energy, metabolism helps the body stay balanced and respond to changes, which is what homeostasis is all about.