Metabolism
Definition of Metabolism
Metabolism is the set of chemical reactions within an organism that enables it to maintain life, grow, reproduce, and respond to its environment. Metabolism includes both the breakdown of nutrients to release energy and the synthesis of compounds necessary for cell function.
How Your Body Gets and Uses Energy
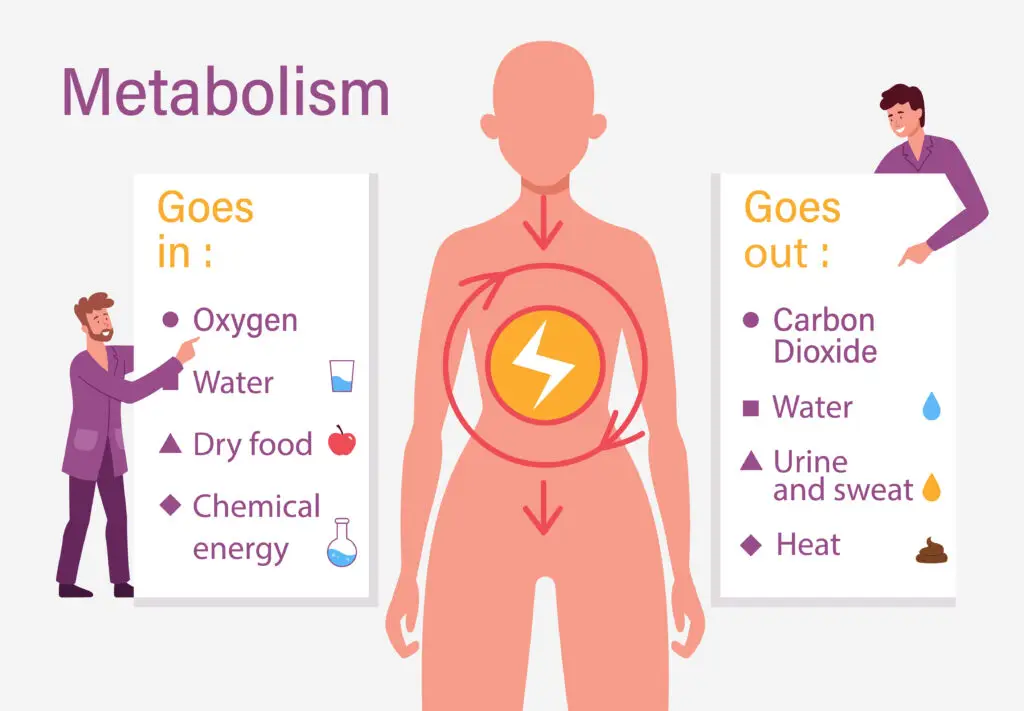
Metabolism is the process your body uses to turn food into energy. Every living thing, from tiny ants to big elephants, has metabolism to power their body. It helps animals grow, move, and stay alive.
How Metabolism Works
Metabolism has two main jobs:
- Breaking Down Food: Your body breaks food into smaller pieces, like sugars and fats, to release energy.
- Building Up: It uses energy to build and repair things, like muscles and bones.
This process happens in your cells and is powered by the food you eat and the oxygen you breathe.
Examples of Metabolism in Action
- Running: Your body burns energy quickly to power your muscles.
- Sleeping: Even when you rest, your metabolism keeps working to help you breathe and repair your body.
- Growing: Metabolism helps kids grow taller and stronger by building new cells.
Why Metabolism Is Important
Metabolism keeps your body running, like fuel for a car:
- Energy for Movement: Helps you run, jump, and play.
- Body Repair: Fixes cuts, bruises, or worn-out cells.
- Temperature Control: Keeps your body warm when it’s cold.
Factors That Affect Metabolism
Metabolism is different for everyone and can change depending on:
- Age: Younger people usually have faster metabolisms.
- Activity Level: Active people burn more energy.
- Diet: Eating healthy foods gives your body better fuel.
Fast vs. Slow
- Fast Metabolism: Burns energy quickly, so people might need to eat more.
- Slow Metabolism: Burns energy slowly, so people need less food.
Both are normal, but staying active and eating healthy can help balance metabolism.