Niche
What is a Niche?
In ecology, a niche is the specific role or function of an organism within its habitat, including its interactions with other species and its use of resources. A niche encompasses an organism’s behavior, diet, and place in the food web.
An Animal’s Job in Nature
A niche is the role or “job” an animal has in its environment. It includes everything the animal does to survive, like what it eats, where it lives, and how it interacts with other plants and animals.
What Makes Up a Niche?
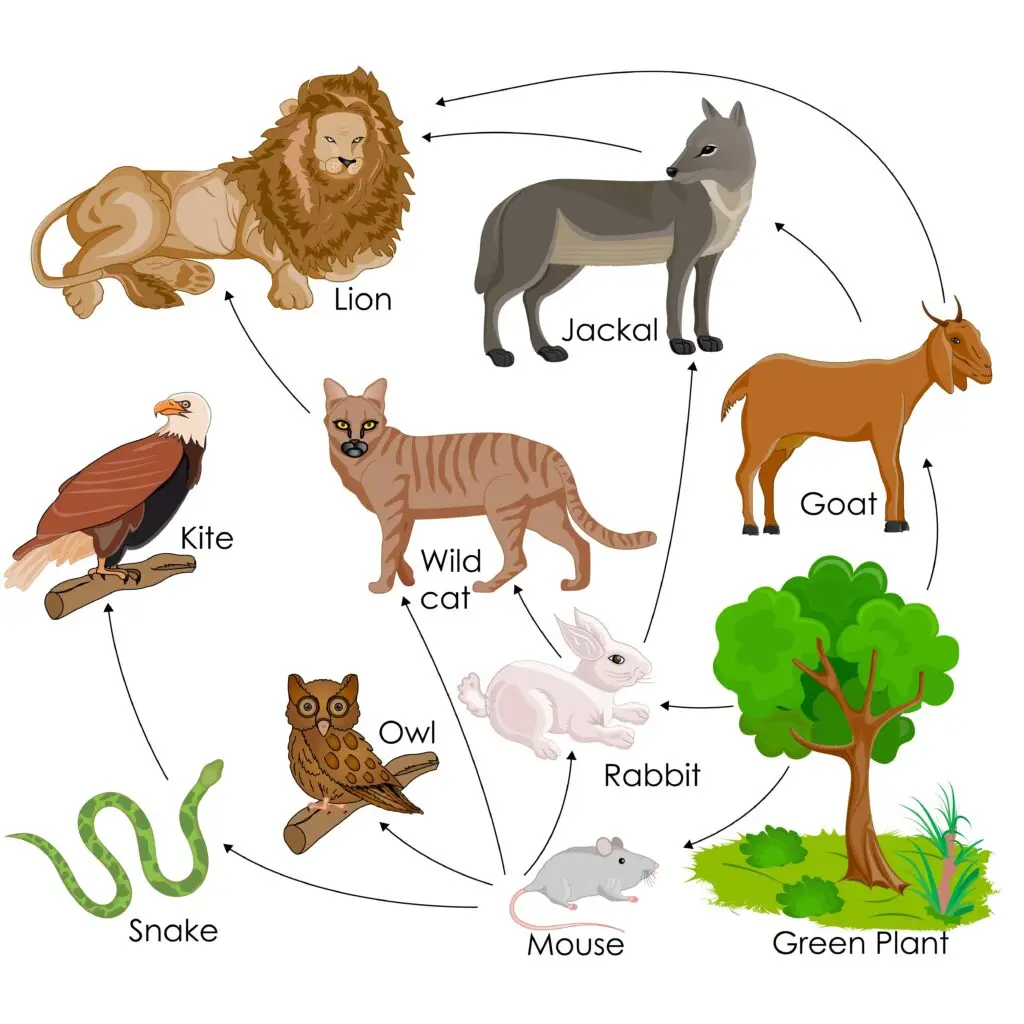
An animal’s niche includes:
- Habitat: Where it lives, like a forest, ocean, or desert.
- Food: What it eats, like plants, insects, or other animals.
- Activity: When it’s active, like being awake during the day (diurnal) or night (nocturnal).
- Interactions: How it affects and is affected by other species, like being a predator, prey, or pollinator.
Examples of Niches
- Bees: Their niche is to pollinate flowers and make honey.
- Wolves: They are predators that control populations of animals like deer.
- Earthworms: Their niche is to break down dead plants and improve soil for other organisms.
Importance to Ecosystems
Every species has a unique niche that helps keep ecosystems balanced. If one species disappears or can’t do its job, it can affect the entire ecosystem. For example, if bees stop pollinating, plants and the animals that eat them might struggle to survive.
How Animals Share Niches
To avoid competition, animals often use different parts of their environment:
- Birds: Some feed on tree insects, while others hunt on the ground.
- Fish: In coral reefs, some fish eat algae, while others eat plankton or smaller fish.